File types or file extensions help Windows identify the apps and software that are needed to open them. These are the MP3s of the world, the DOCXs, the JPGs, the TXTs, and hundreds of other file formats that your PC can recognize. And, safe to say, if your computer can recognize a file, it has a file type.
But sometimes, you may want to change the extension of a file, say, to make Windows open it with a different app. Well, here is everything you need to know about changing a file type in Windows 11.
How to change a file type in Windows 11
There are a few ways that you can change a file type in Windows 11. You can also change the file type of multiple files as well with a few commands. Let’s take a look at all these ways separately so you can easily navigate through them for your exact purpose.
Related: How to Clear Space on Windows 11
Method #01: Using Rename
The simplest way to change a file type is by renaming the file itself. But before we begin, you will have to have the file extensions enabled from the ‘View’ folder options. If you already have it enabled, skip this bit. For everyone else, here’s how to do it:
Press Win + E to open File Explorer and click on View.

Then select Show, and then click on File name extensions such that there’s a check placed next to it.

You will now see the extension of a file at the end of its name.

To change the file type, select this file and click on the Rename icon.
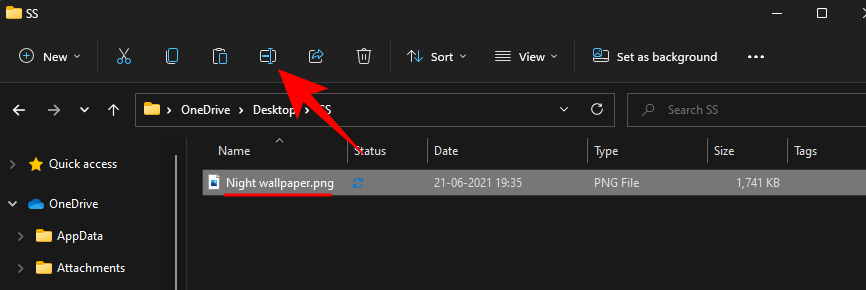
Now, change the file extension (everything after the last dot) to the one that you want.

Press Enter. When asked if you’re sure about the change, click Yes.

Note that you can’t just change a file type to any other file type. For instance, you can’t change a .doc file to a .wav file. One is a document file while the other is a waveform audio file. The two file types have to be associated or be similar enough in order for the file to still open after renaming.
Related: How to Clean Registry on Windows 11 [4 Ways]
Method #02: Using ‘Save As’
Another way to change a file type is by saving it in another format from an app that lets you do so. Programs from the Microsoft Office Suite (Word, Excel, etc.), Paint, Text Editor, etc. let you export your files into a different format. This works so long as the exported format is related to the default save format of the program and is available from the list of formats in the app.
For instance, you can easily save a Word document as PDF, or a text file as a BAT file. Let’s take the former as an example so you know how this is achieved:
Open the file in its default program (a document file in MS Word). Then head to the File option (most programs will have a similar option).
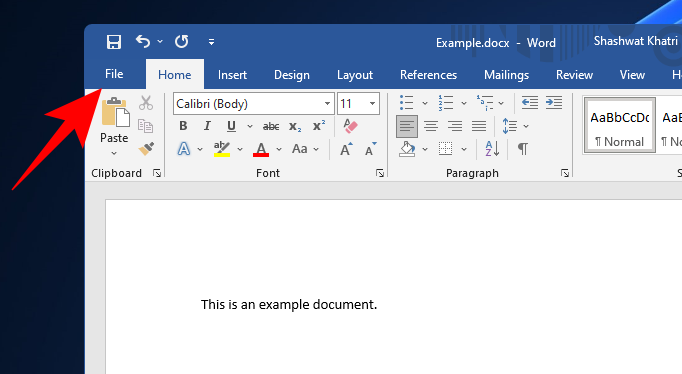
Select Save as.

Choose a location to save your file.

Next to “File name”, enter the name of the file as you wish. Then next to “Save as type” click on the drop-down menu.
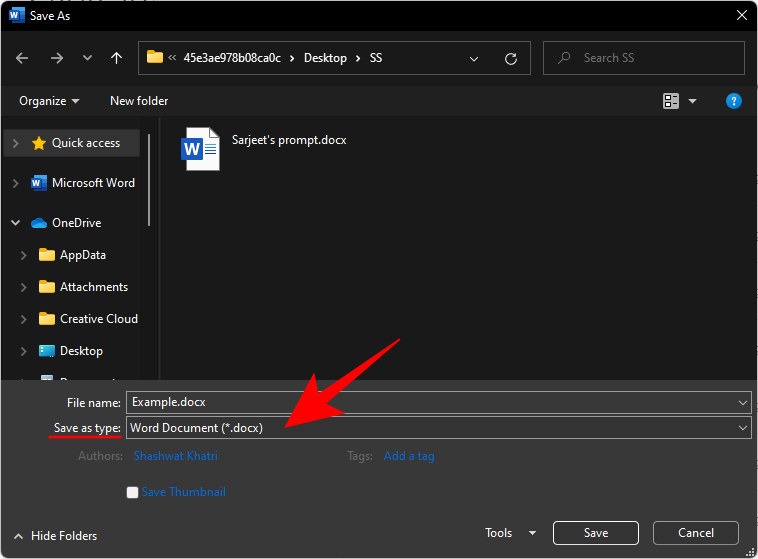
Select the file type that you want.
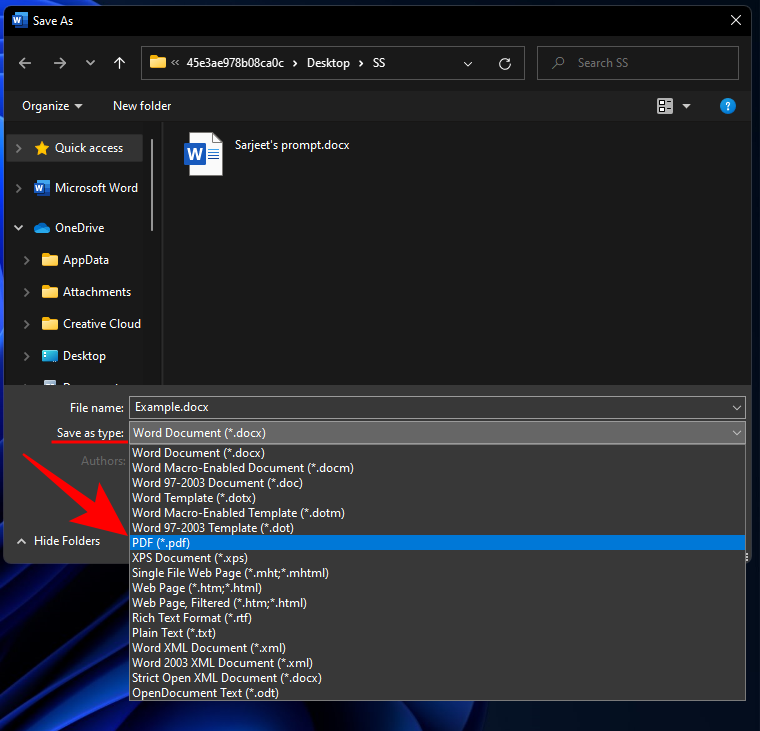
Click on Save.

You have now changed the extension for your file. This method works for all applications that let you save your files in a different type. If you don’t see the file extension that you want to save your file in, then you may benefit from the methods mentioned below.
Method #03: Using Command Prompt
With the Command Prompt, you can change the extension of a single file as well as multiple files, all in one go. First up, let’s take a look at how you can do so for a single file.
3.1 For a single file within a folder
Navigate to the folder that contains the file whose extension you want to change. Right-click on it and select Copy as path.
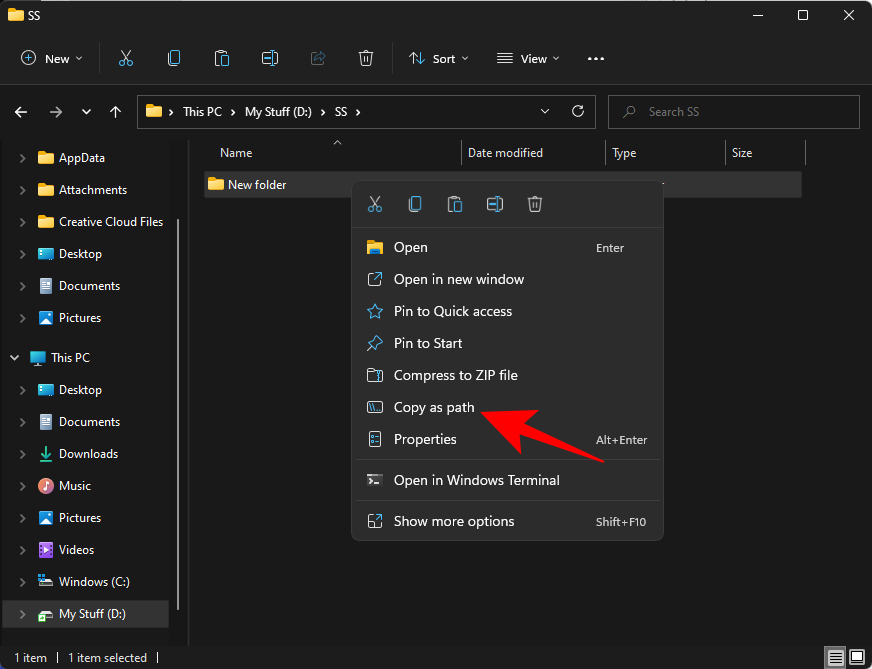
Now press Start, type cmd, and select the Command Prompt application.

Type cd /d and then press Ctrl + V to paste the folder path that was copied earlier. It should look something like this:
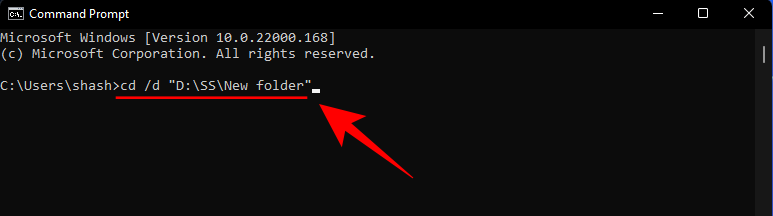
Press Enter. This will change the directory to the folder that contains the files.

This means that all the changes made henceforth will be made to the files that are immediately within this folder.
Now type the following command for the file extension that you want to change. Make sure to change the files and their extensions appropriately for your files.
rename "file-with-extension-1" "file-with-extension-2"
In our example below, we’re changing the extension of the file “Image 1.jpg” to “Image 1.png”. So the command will look something like this:

Note: When typing a file name that contains a space in it, enclose the full name of the file within quotes, as done in our example.
3.2 For multiple files within a folder (batch)
Now, let’s take a look at how to change the file extension of all the files that are within a folder.
Open the Command Prompt and change the directory to the folder that contains the files whose extensions you want to change (as shown before). Then, type the command as given below with the existing file extension and the new file extension:
rename *.extension1 *.extension2
Again, make sure to change the extensions accordingly. Then press Enter. sdf In our example below, we’re changing all the JPG files to the PNG format.

As soon as you hit Enter, the extensions of all the files within this folder will be changed to the new extension.
3.3 For multiple files (and save the original)
If you want to change the extension of a file but want to keep the original file intact, here’s the command that you need to type:
xcopy *.extension1 *.extension2
Press Enter. Once again, the extensions used above are just for demonstrative purposes. You should replace these extensions as per your needs.

3.4 For multiple files (regardless of the extension)
Finally, if you want all files within that folder to change to the new extension regardless of what their original extension is, then type the following command:
ren *.* *.newextension
Press Enter. Make sure to replace “newextension” with the actual file extension that you want. In our example, it’s PNG, so it looks like this:

3.5 For multiple files (including files in all sub-folders)
You can also use a command line to change the file type of all the files within a folder, including those that are in the sub-folders. Here’s how to do so:
Open the Command prompt and change the directory to the target folder that contains the files (shown before). Then, type the following command:
for /R %x in (*.ext1) do ren "%x" *.ext2
Make sure to replace ‘ext1’ with the current file extension and ‘ext2’ with the new file extension. In our example, we’re changing JPG to PNG.

A few things to note when using commands to change file extensions – make sure to enter the commands correctly. To be on the safer side of things, you may want to back up the files to a different folder, you know, just in case you make an error or things don’t pan out as planned.
Method #04: Using Online Services
If you’re not able to view the contents of your file after changing its type or if you don’t have the app to save it as a different type, you can always resort to free online services that let you do so. They help convert one file type into another and, depending on the file types and the service that you’re using, may even offer additional options like compressing the file to make it smaller.
Because there are tons of file types out there and just as many online services to convert them, it’s not feasible to recommend one or the other. A quick Google search should avail you of a few sites for your purpose.

What happens when you change a file extension?
When you change a file’s extension, you tell your PC that you’re changing the way the file is read. However, it doesn’t change the way that file is formatted. For instance, if a file is in the MPEG (mpg) format and you change it to PNG or any other unrelated format, it won’t suddenly become an image and open in Photos Viewer.
You may modify the file extensions to make Windows open it in another app. But if the app can’t read the format in which the file was originally rendered, then it will register an error. This is why sometimes you may not be able to open them after changing the file type.
How to set default apps for file types in Windows 11
Usually, it isn’t recommended to change the file type in which it was formatted as this makes it problematic for some apps to parse the file. If you’re changing a file extension only because you want to open it in a different app, you could instead just change the default app for that file type.
To change default apps for a file type, follow the steps below:
Press Win + I to open the Settings app. Then click on the search bar on the left. type “default app”, and select Choose a default app for each file type.

Here, you will find a long list of file types to set default apps for. Click on the search bar above and search for a file type.
Click on the search result.

Select the app that you want to set as default for this file type.

If you don’t find an app here, click on “More apps” to reveal additional apps options.

We hope you were able to change one file type into another with the methods mentioned in this guide. Doing so comes in handy when you want Windows to use the right app to open a file. Just make sure to turn on file extension visibility and enter the commands as given. If possible, back up your files too.
RELATED
- How to fix Windows Insider Program options greyed out issue on Windows 11
- Laptop Hotkeys Not Working on Windows 11? How to Fix
- How to Reset BIOS in Windows 11
- How to Check Battery Health Windows 11
- 18 Ways to Fix 100% Disk Usage on Windows 11
- How to Wipe a Hard Drive on Windows 11
- How to Ungroup Icons on Windows 11 Taskbar With a Registry Hack
- How to Move the Taskbar to Top in Windows 11
- How to Create a Restore Point in Windows 11