One of the niftiest (if not the most) features available on Windows 11 is the hibernation mode. Although it is not available outright by default, enabling it can help you save your battery, if you are working on a laptop, and manage your system’s power consumption efficiently? If these questions are popping into your head, we’ve got you covered.
Our detailed guides below will take you through all the bits and pieces of this wonderful feature and familiarize you with its workings and most importantly, how to turn it on.
What is the hibernate mode in Windows 11?
Just like its definition in the dictionary, the hibernate mode in Windows 11 puts your system in a low-power mode, somewhat similar to sleep mode. However, unlike sleep mode, the hibernate mode consumes less power and preserves battery life. When put on hibernation mode, your system shuts down all background activity, and ongoing work before taking a “snapshot” of data and saving it onto your hard drive. The next time you turn on your system, you can automatically resume your previous work right where you left off without any hindrance.
This is particularly useful if you are not actively using your device or are starting to run low on power if you are working on a laptop. So, let us now go through the different ways through which you can enable this handy feature on your system.
Related: Top 8 Ways to Disable Notifications on Windows 11 (and 3 Tips)
How to enable hibernate mode in Windows 11 in 3 ways
As mentioned before, the option to enable hibernate mode is not available by default in Windows 11. We will have to turn it on manually using three (well, technically five) different methods. Every method presented in this guide is 100 percent safe and should get you into hibernation mode in no time at all. Let’s get started.
Method 1: Using Control Panel
The Control Panel allows you to fiddle with many different settings of your system, hibernation mode included. There are three ways you can achieve this. Let us go through them, one by one.
Open the Control Panel by going to the Start Menu search box or simply clicking on the Search icon and typing Control Panel in the search box.
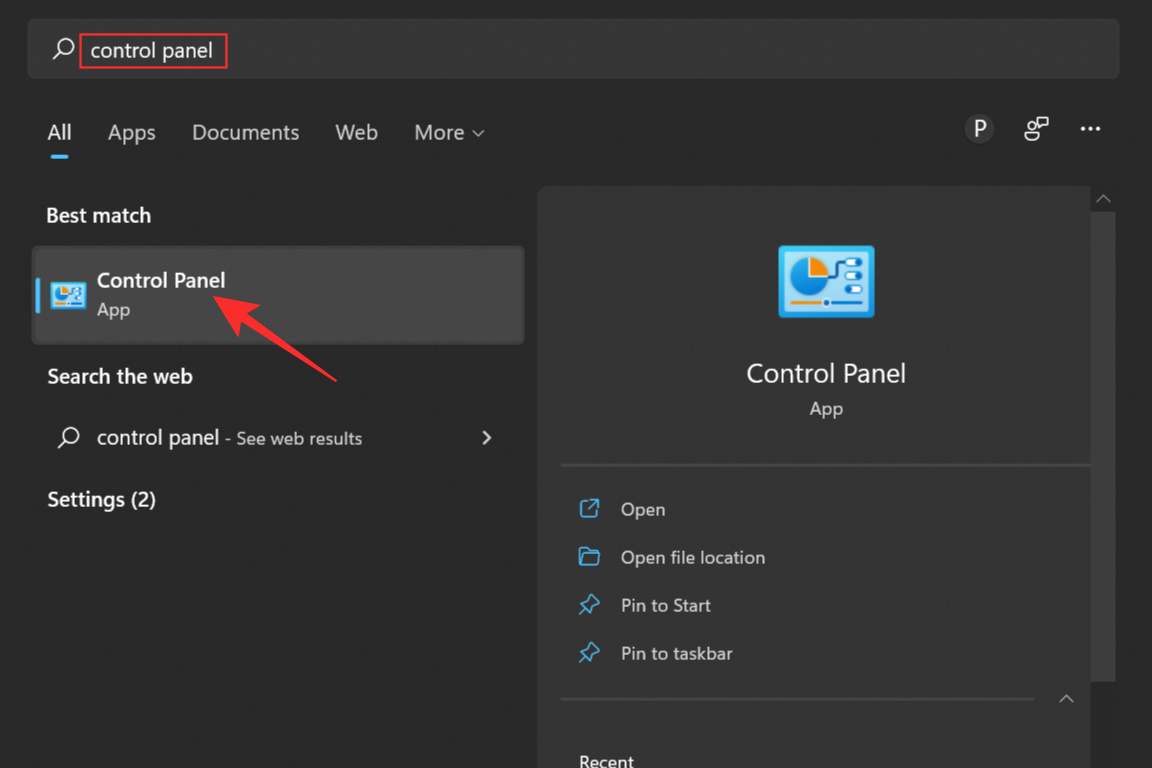
Open the Control Panel by clicking on it. Now select System and Security from the list of options.
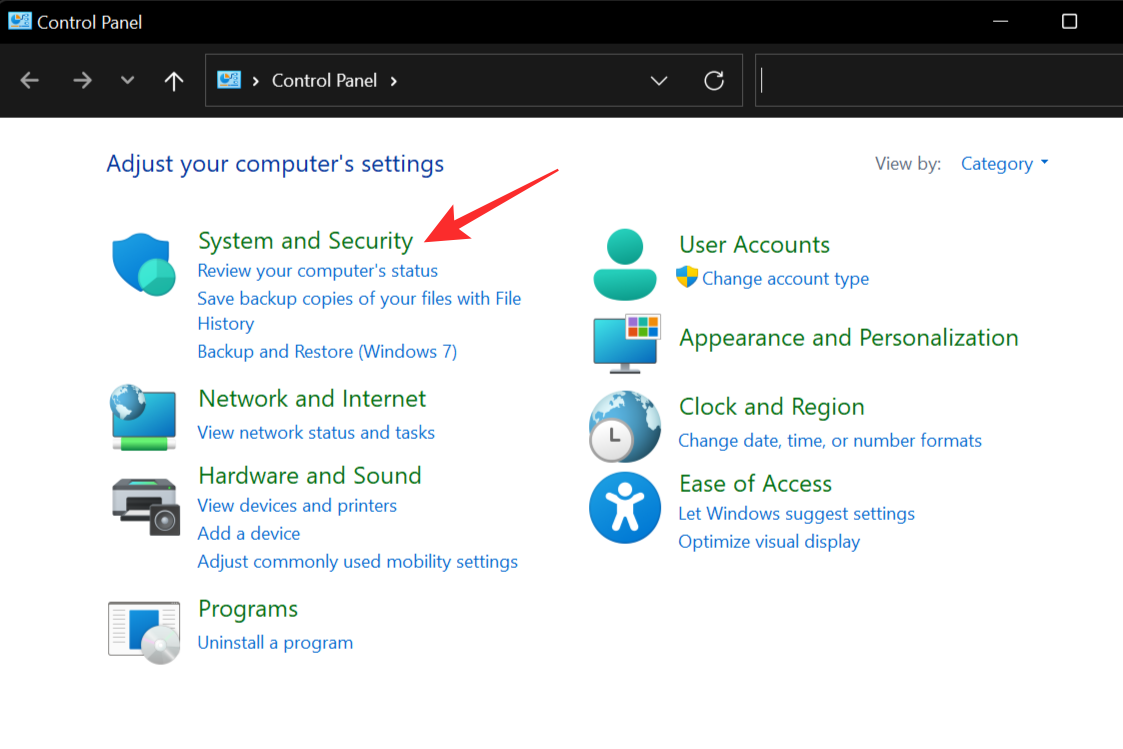
Click on Power Options to bring out the power options menu.
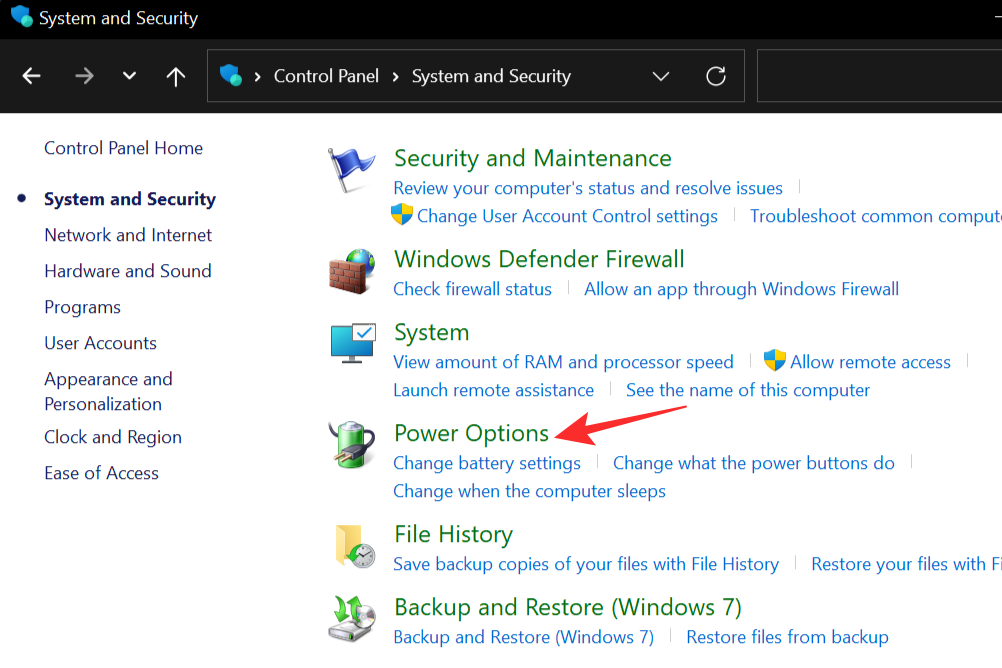
On the left-hand tab, select Choose what the power buttons do.
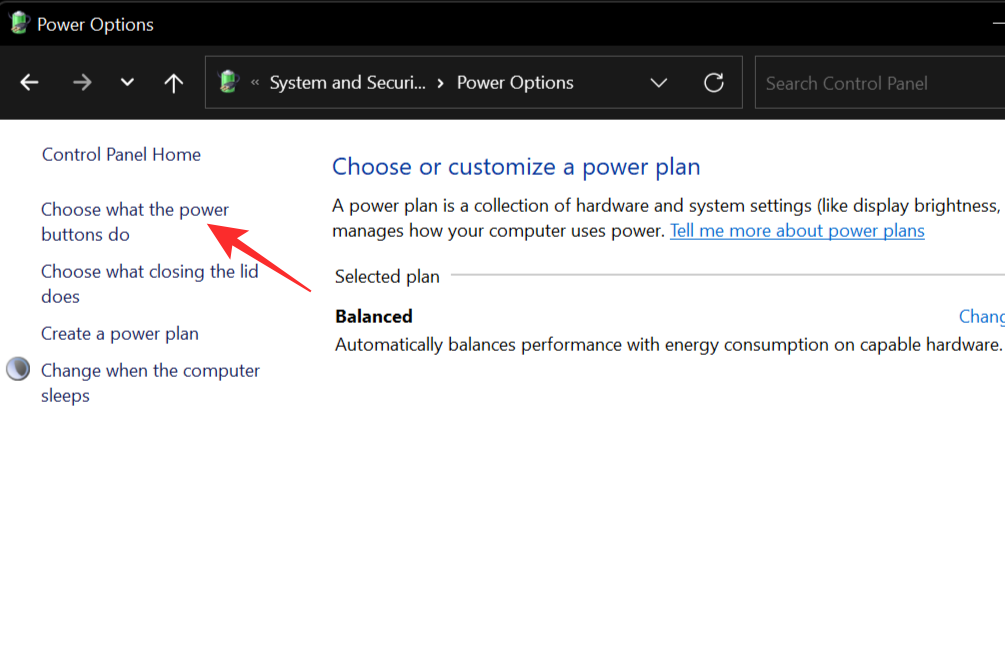
This will open up a new settings window. Click on the Change settings that are currently unavailable option.
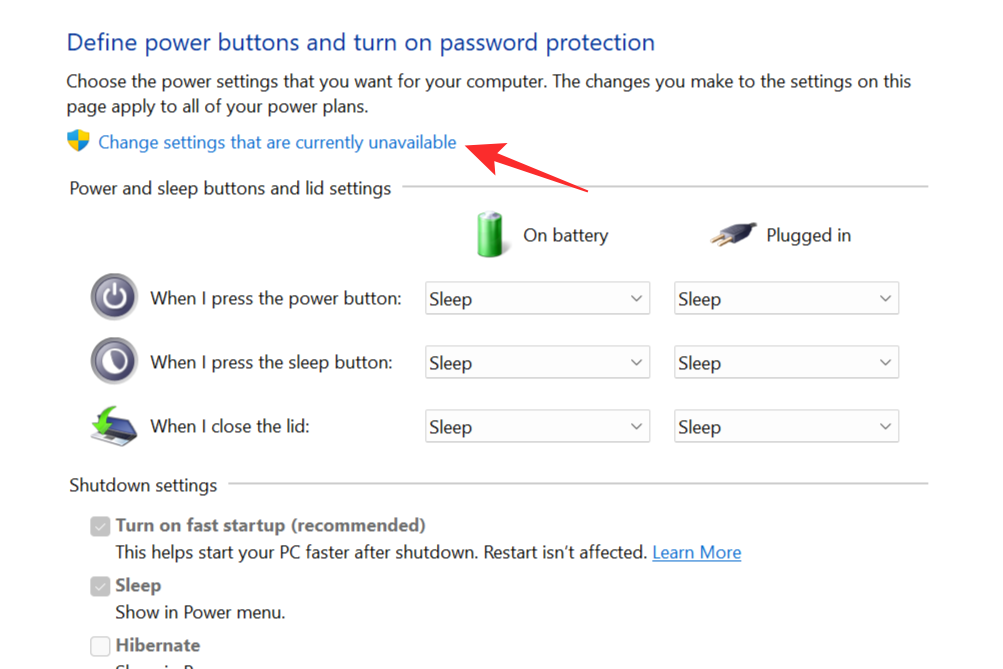
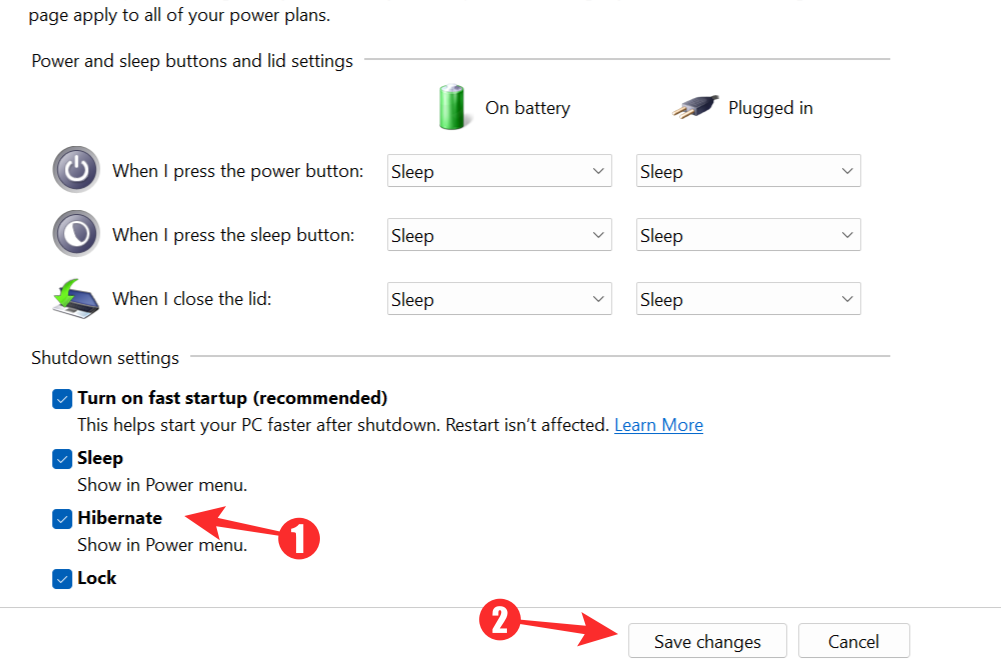
The settings that were not interactive before will become so. Check the box next to the Hibernate option. This will allow the Hibernate Mode to show up on the Power Menu. Click on Save changes to complete the process.
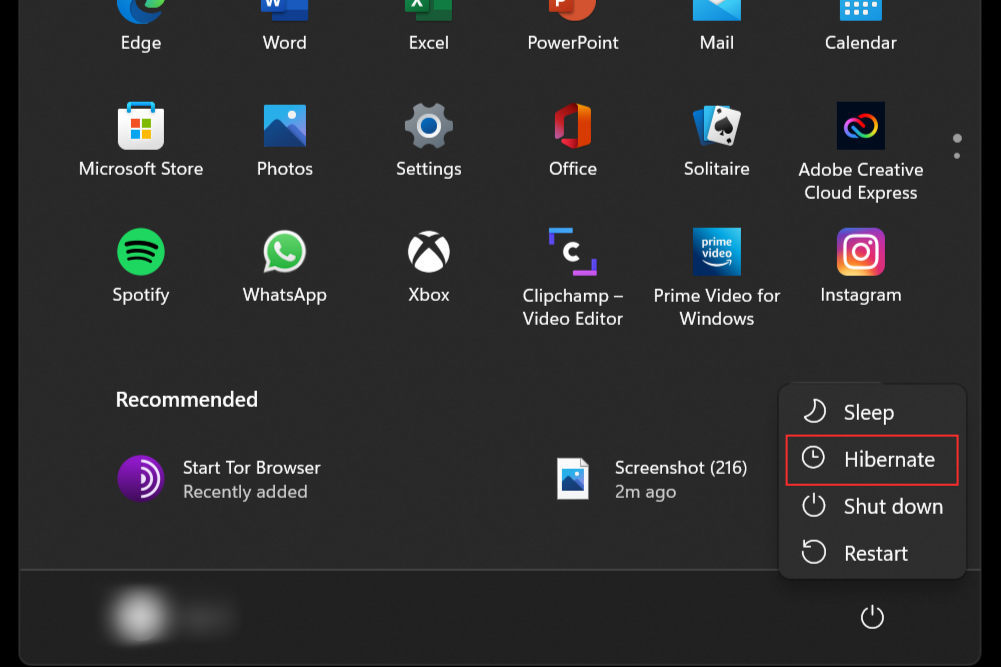
Now go to your Windows Start Menu and click on the Power button. The option for hibernate mode should be available.
Tip 1: Configuring Hibernate on the Sleep or Power button
This method is very similar to the previous one. Using this method you can simply choose to go into hibernation mode at the push of a button – the power button on your system, to be specific.
Follow the steps from the previous method to access the Control Panel and open the power options menu. Now select Choose what the power buttons do.

In the next window, click on the drop-down menu next to the When I press the power button line and choose Hibernate. Select Save changes to save your settings and close the window.
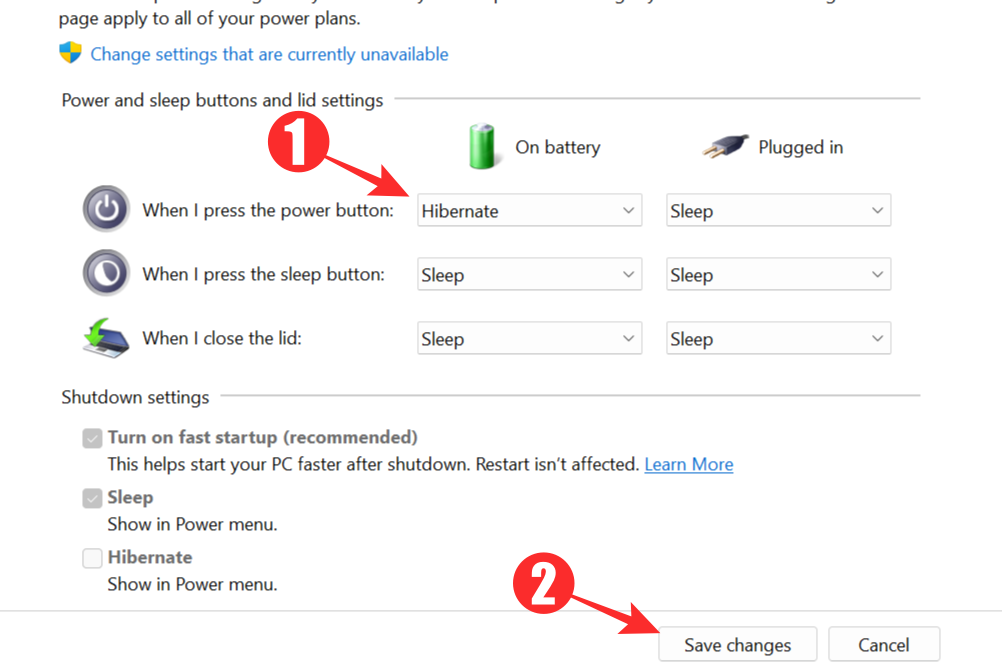
Whenever you press your power button, your system will automatically revert to hibernate mode from now on.
Tip 2: Hibernate when ‘closing the lid’
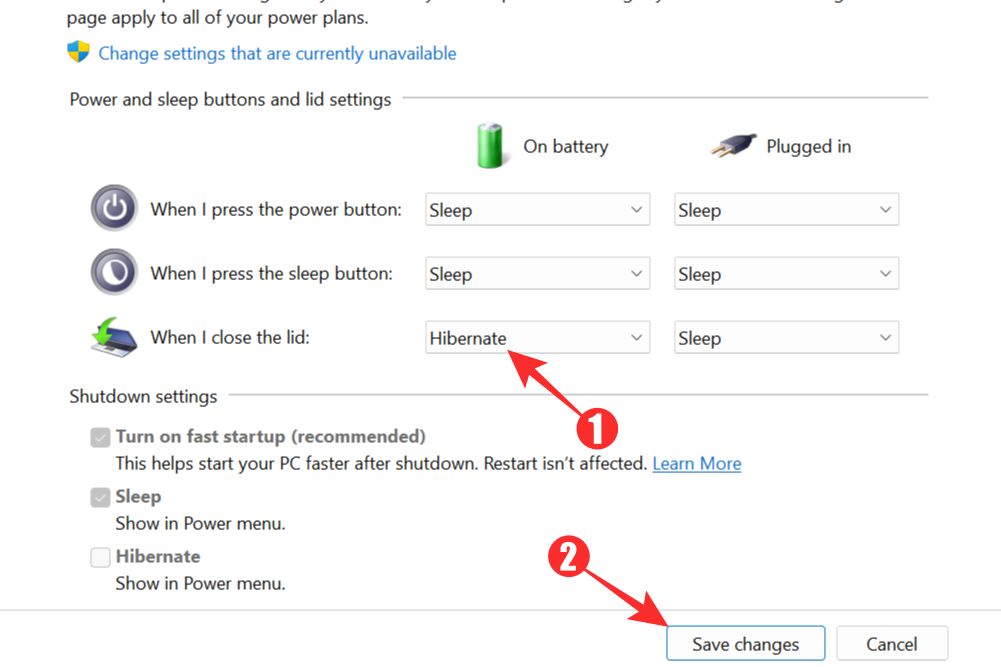
The last method will cause your system to switch to hibernation mode whenever you close your lid (if you are working on a laptop, that is). The steps are similar to the previous methods. You will need to open Control Panel and access the power options menu. Click on select Choose what the power buttons do again.

This time, choose Hibernate from the drop-down menu next to the When I close the lid option. Save your changes and you should be all set.
Related: How to Disable Onedrive on Windows 11
Method 2: Using Command Prompt
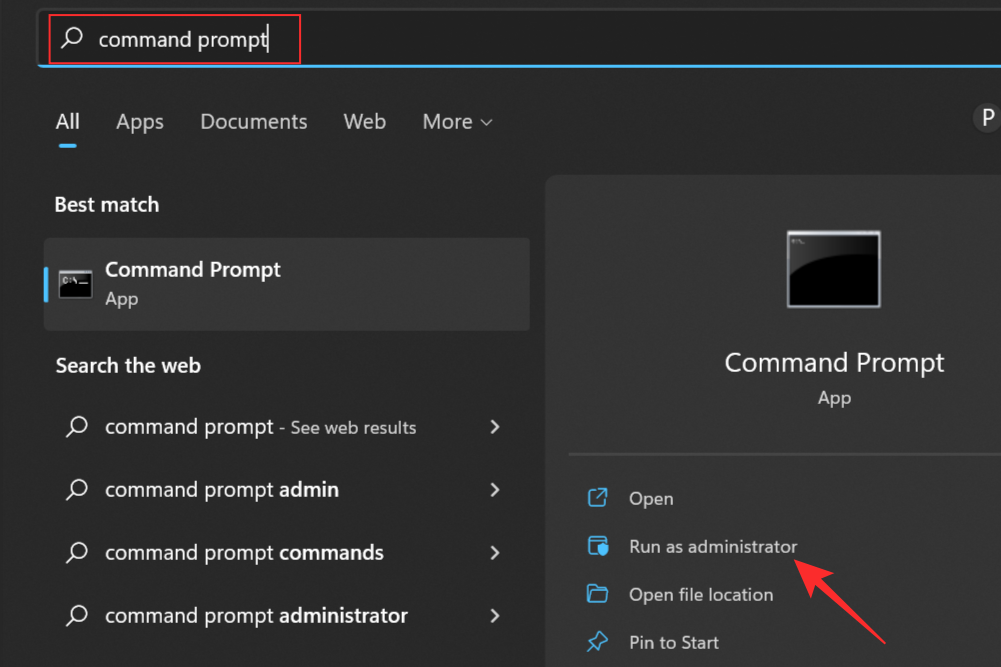
If using the Control Panel method is a little too long or bothersome, you can turn to Windows Command Prompt to get the job done. In the Windows Start Menu or the Search Menu, type Command Prompt in the text box and hit enter. From the search results, run Command Prompt as administrator.
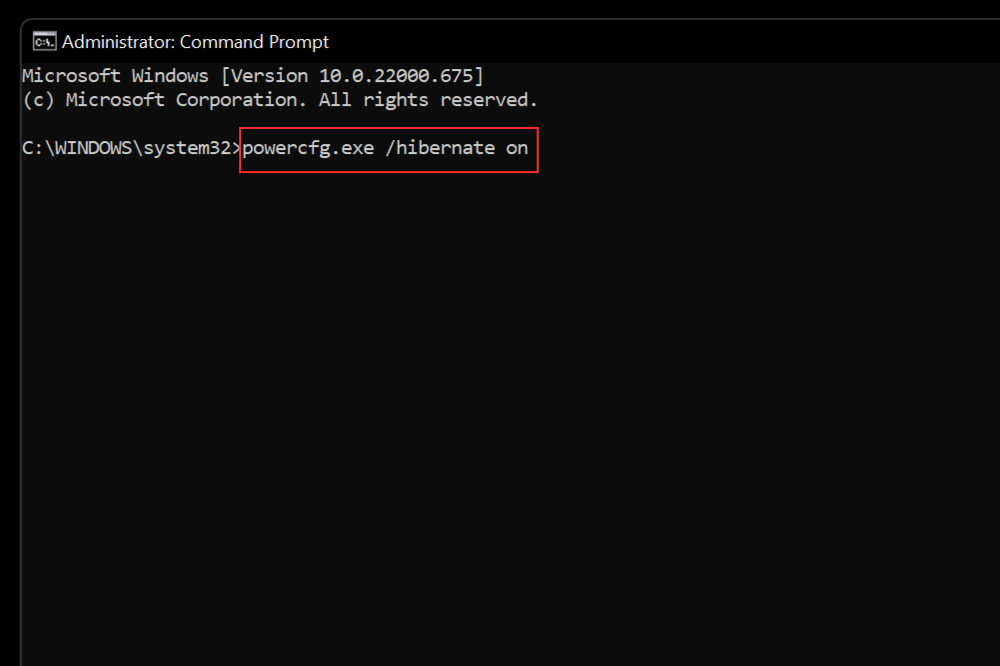
 Now, type in the following command and hit Enter to enable hibernate mode:
Now, type in the following command and hit Enter to enable hibernate mode:
powercfg.exe /hibernate on
Related: How to Stop Popups on Windows 11
Method 3: Using Windows Registry
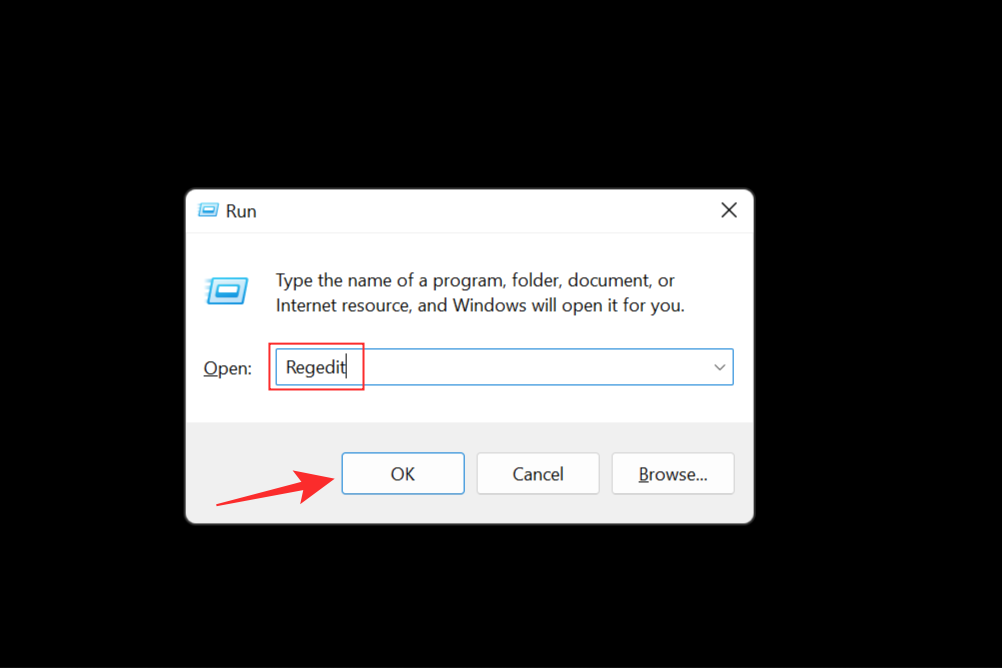
You can also use Windows Registry if the previous methods don’t have the desired results. Press the Windows+R key to bring up the Run dialog box. Type in Regedit and press OK to open the Windows Registry Editor.
Now that you have access to the Registry Editor, navigate to the following link: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Power.
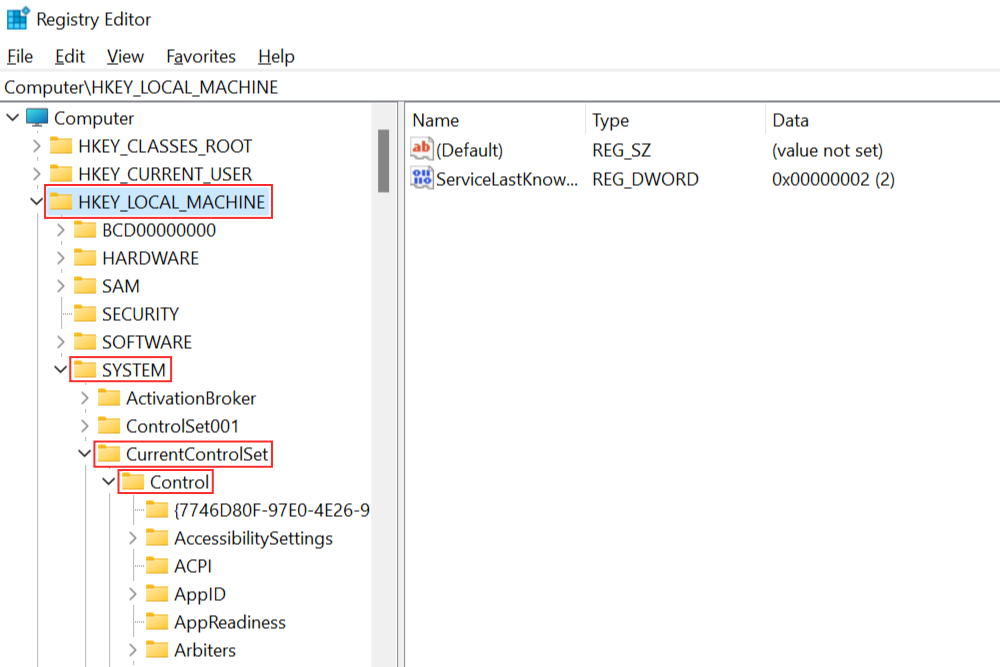
You will have to scroll a fair way down to find the Power link.
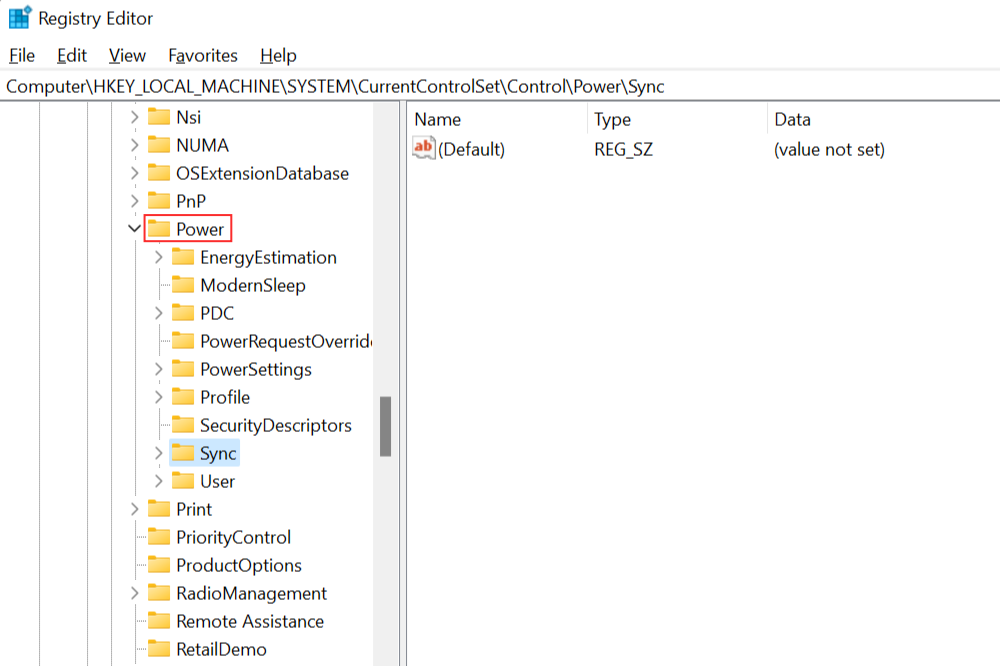
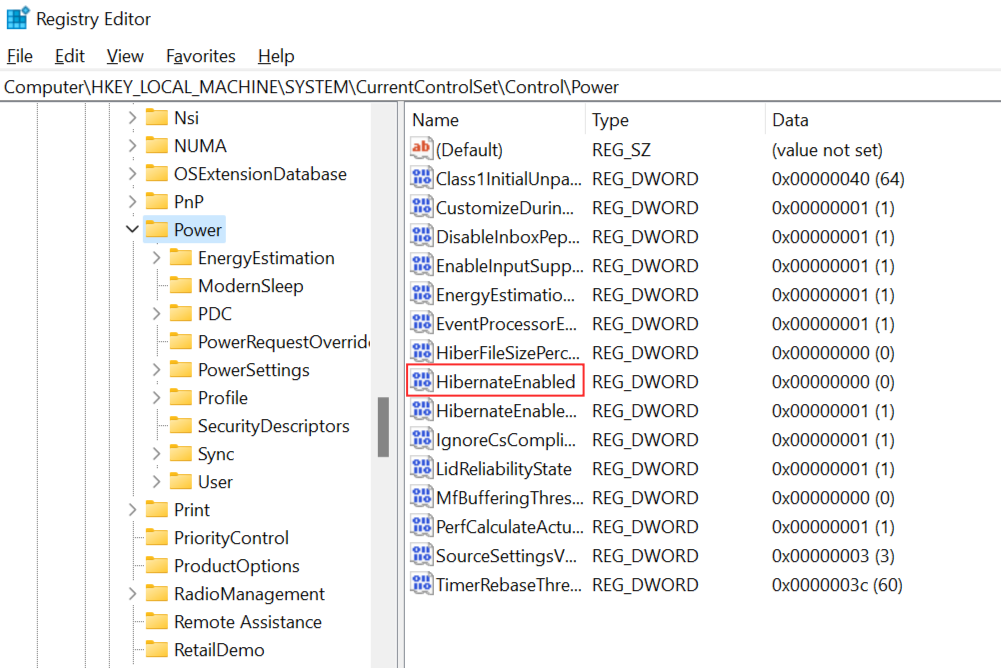
On the right panel, double-click on HibernateEnabled.
This will bring up the Edit DWORD Value box. Change the value to 1 to enable hibernate mode and click OK.
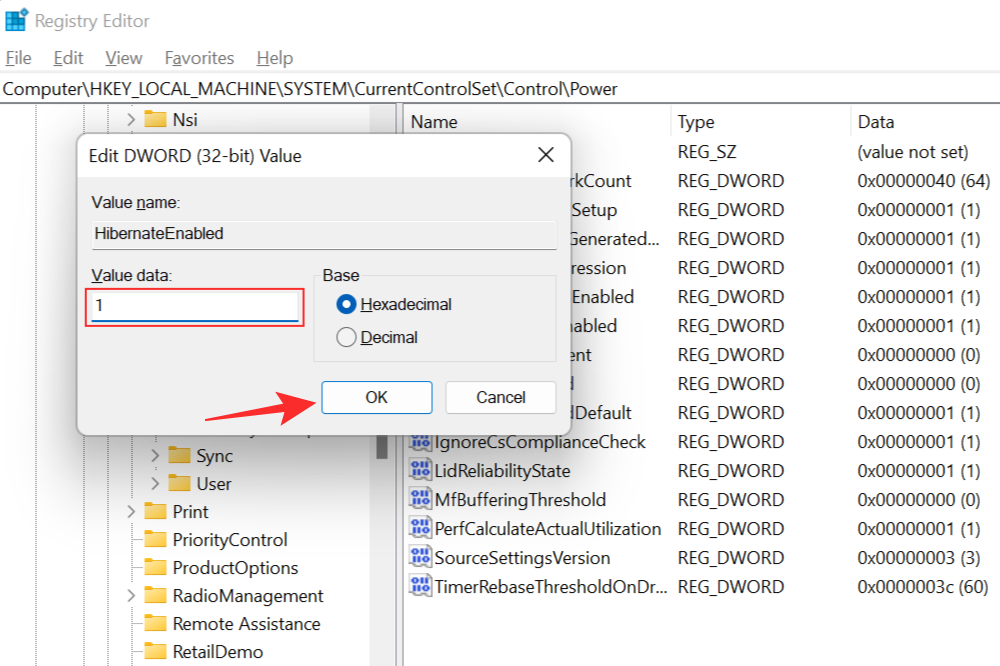
You will have to restart your system for the changes to take effect. Once restarted, you will find that hibernate mode is enabled on your system when you access the Start Menu.

How to change ‘hibernate after’ duration
Should you choose to, you can set a specific timer after which your system will automatically go into hibernate mode. To access this feature, you will need to open the Control Panel and go to System and Security.

Now select Power Options to access power settings.

Click on the Change plan settings.
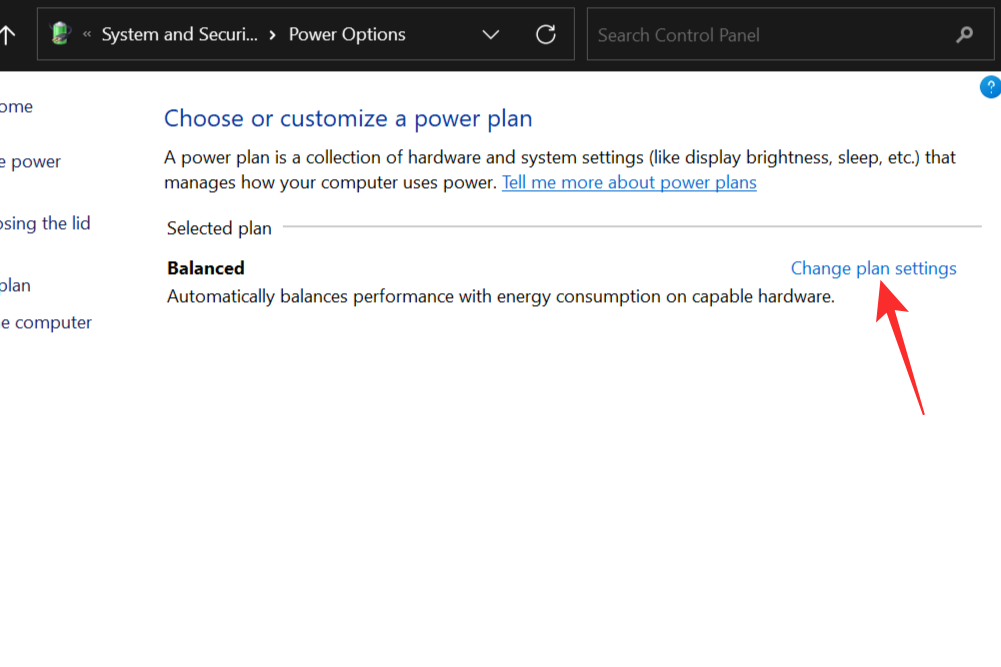
Select Change Advanced power settings.
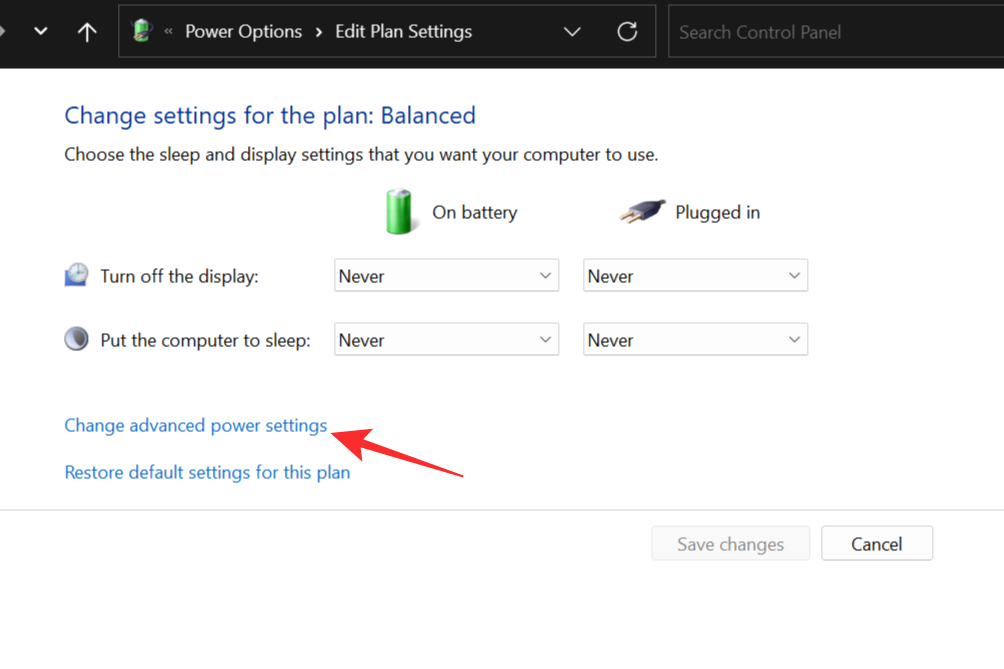
In the Power Options window that pops up, double-click on Sleep to explain its settings.

Double click on Hibernate after option now.
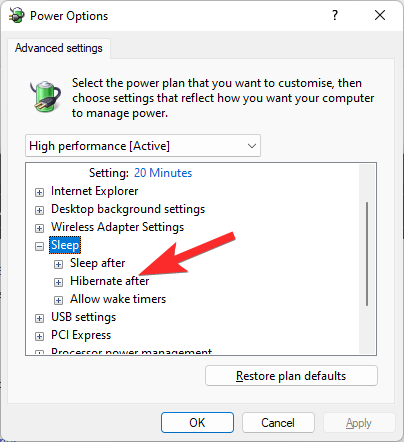
Now, click Never. (Or any other value that you see there. It is based on the power plan currently selected.)
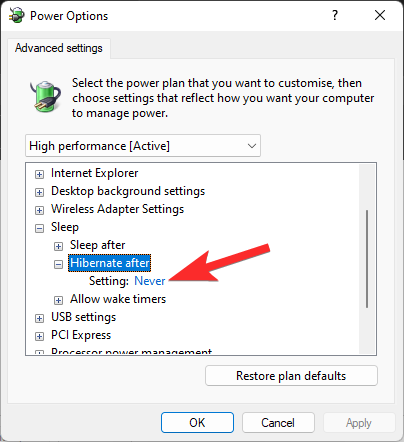
Set the value (in minutes) you want to make your PC go to hibernate after. If you want your PC to go to hibernate automatically after 90 minutes, then simply enter 90 as the value here and then click Apply. If you wish to never hibernate your PC automatically when it is idle, use the value 0 (zero) here.

Now click OK to complete the process.
Your system will now automatically hibernate after a set time limit of inactivity.
How to “wake up” the system from hibernation
You can wake up your PC from Hibernation mode by simply pressing any key on the keyboard or using your mouse. If you are using a laptop and have shut the lid as the system hibernated, simply opening up the lip would wake up your device from hibernation mode. In case this does not work, pressing the power button should do the trick.
How to disable hibernation mode in Windows 11 in 3 ways
Disabling hibernation mode in Windows 11 is as simple as retracing the steps you took to enable it. Going back and reverting the changes you have made should disable hibernation mode. We have already discussed five ways to turn on hibernation mode in Windows 11, which means that there are five different ways we can turn it off.
Method 1: Using Control Panel
You will need to access the Control Panel again for this method. Use the Start Menu or Search option to open Control Panel.

From the next window select, Systems and Security

Now go to Power Options to bring out the power options menu.

From the left-hand panel of the new window, select Choose what the power buttons do.

In the new window that appears, select Change settings that are currently unavailable.
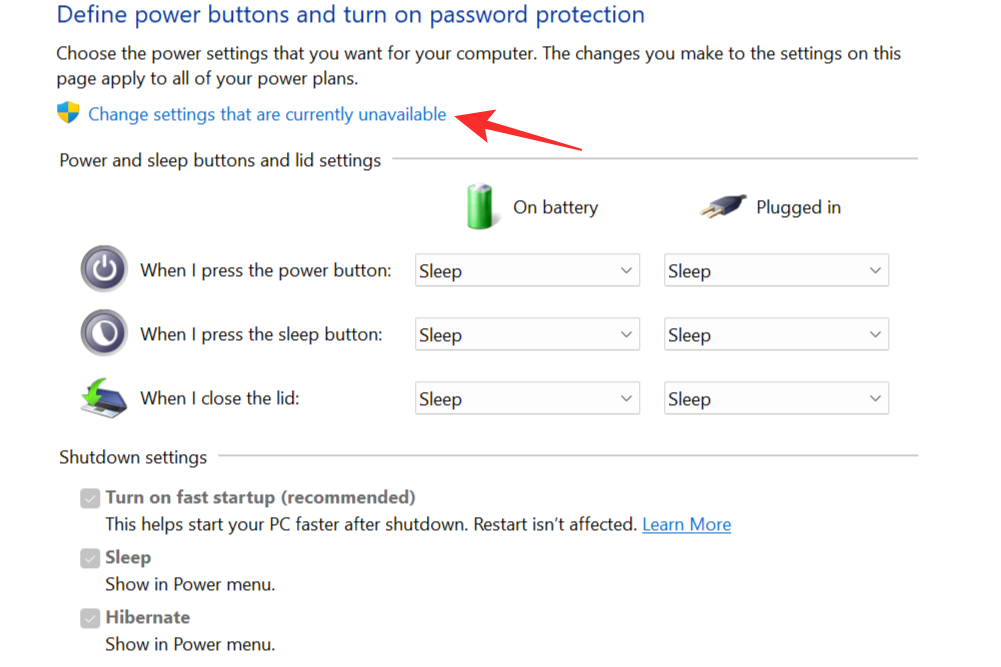
Uncheck the Hibernate option and click on Save Changes to remove hibernation mode as an option from the Start Menu.
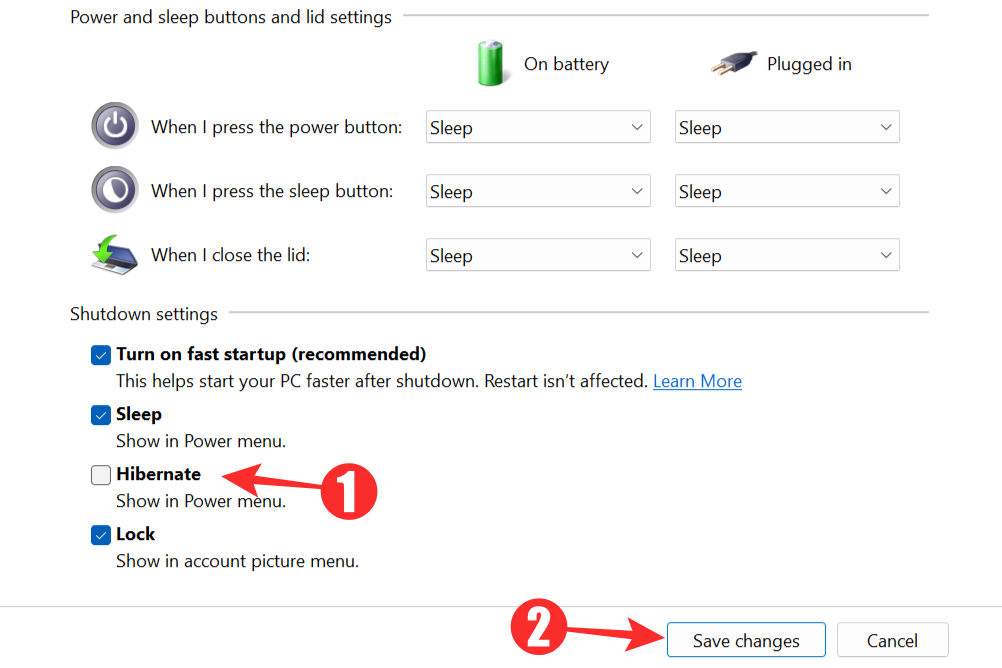
Tip 2: Disable hibernate on the Power or Sleep button
This method is similar to the previous one. You will need to open Control Panel again and access the Power Options. Click on Choose what the power buttons do. Now, click on the drop-down menu next to When I press the power button option and choose any option other than hibernate.
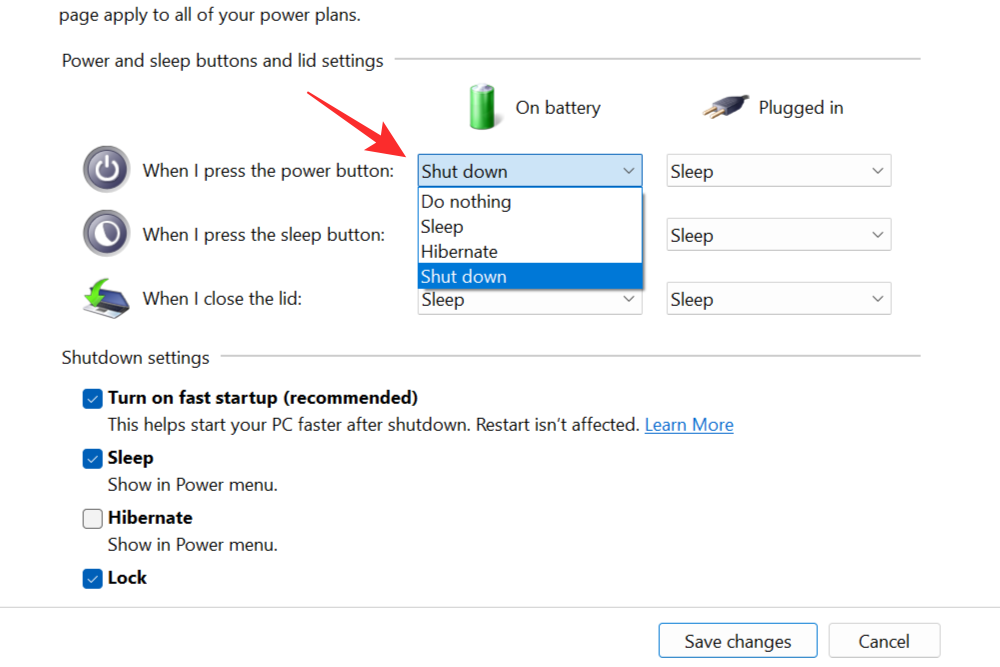
Now click on Save Changes to disable hibernation mode whenever you press the power button.
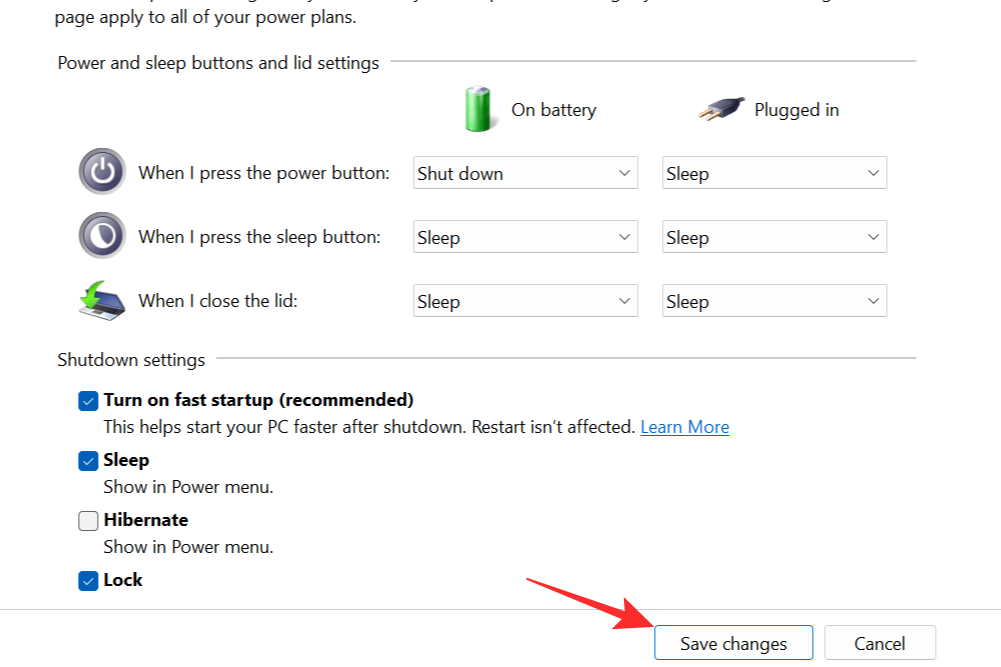
Tip 2: Disabling Hibernate when ‘closing the lid’
Open the Control Panel as shown before and follow the same steps. After selecting Choose what the power buttons do, click on the drop-down menu next to When I close the lid and select an appropriate option other than hibernate.
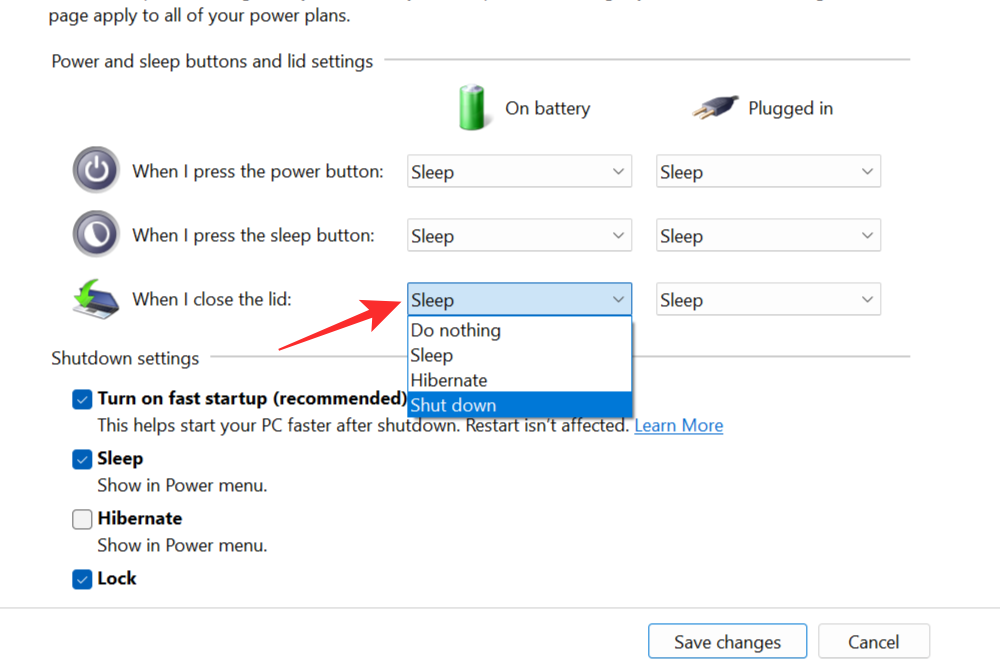
Select Save Changes to disable hibernate mode whenever you close your laptop lid.
Method 2: Using Command Prompt
Command Prompt can be used to turn hibernation off in the same way we enabled it. In the Windows Start Menu or the Search Menu, search for Command Prompt and run it as administrator.

Type in the following command and hit Enter to disable hibernate mode:
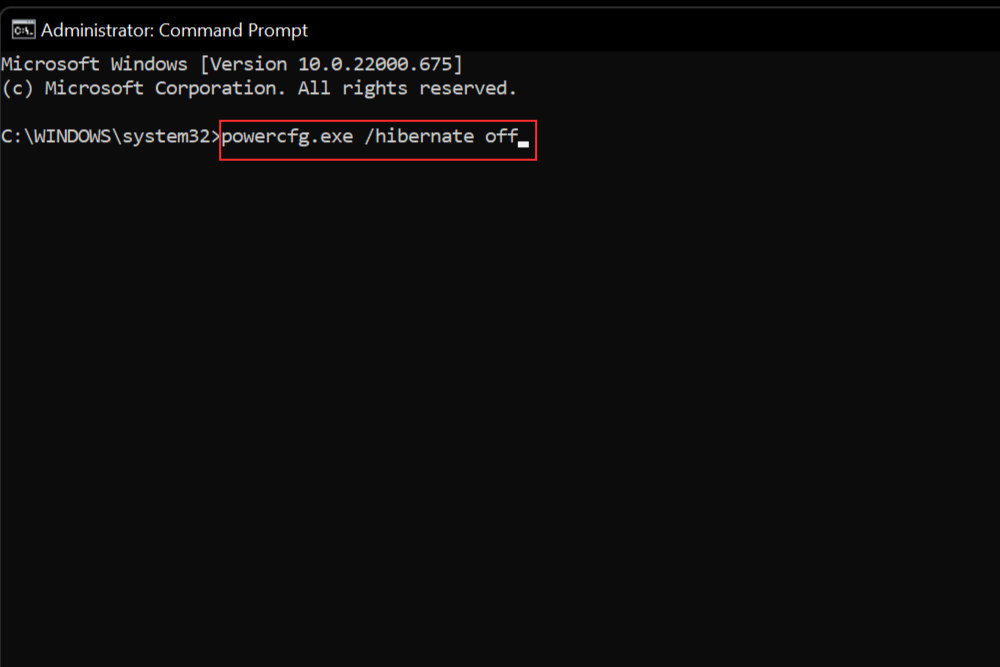
powercfg.exe /hibernate off
Method 3: Using Windows Registry
Open the Run dialog box by pressing the Windows+R key. Type Regedit and press OK to open the Windows Registry Editor.

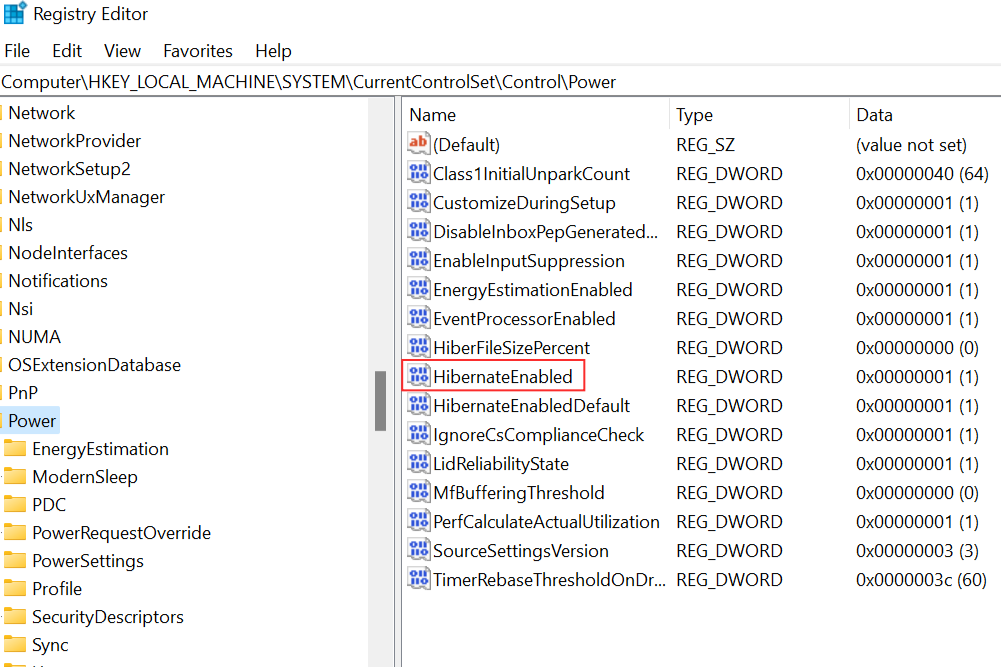
Navigate to the following link in the Registry Editor: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Power.

Scroll down to find the Power link.

Double-click on HibernateEnabled in the right-hand panel.
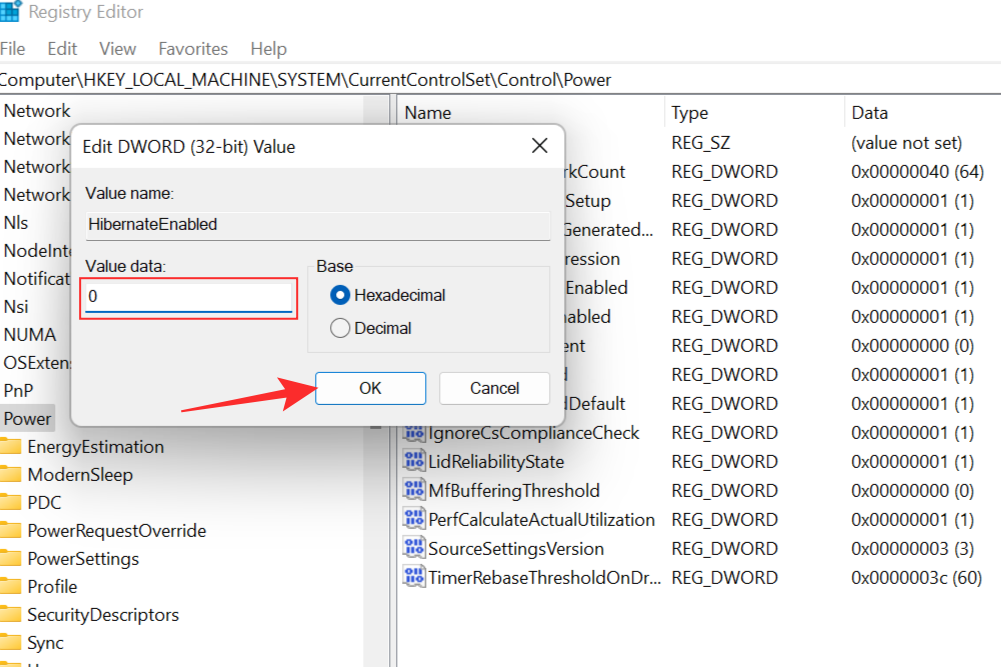
This will prompt the Edit DWORD Value box to pop up. Change the value to 0 to disable hibernate mode and click OK.
Troubleshooting common Hibernation issues on Windows 11
Putting your system in hibernation mode should not cause any problems; rather, it should a handy feature that enhances your experience. Nevertheless, some issues may pop up from time to time when it comes to waking up systems from hibernation mode. These common problems can be easily handled and discharged with the right knowledge. Therefore, we have provided a comprehensive troubleshooting guide to common hibernation issues in Windows 11.
In case your system refuses to wake up from its hibernation mode, you may have to remove the laptop battery to enable a proper discharge of power. Once you have removed the battery, press and hold the Power button for 30 seconds. Now return the battery to its position and connect your laptop to a power supply. Pressing the power button will restart your system and wake it up from hibernation mode.
You can also try pressing and holding the power button down for 10 seconds to wake the system from hibernation mode.
Another common method is to remove the battery and connect the laptop directly to a power supply and power it up. This should restart the system without any issues. You can then proceed to shut down the system, replace the battery and resume your work.
FAQs
Here are our answers to the common queries about hibernation on Windows 11.
Advantages of using Hibernation mode
Using the hibernate mode has many advantages. It can be considered to be an advanced power-saving mode that ensures longer battery life than say, Sleep mode. This is possible because upon hibernating, the system completely powers off and doesn’t consume any battery power. It also means that every single data you were working on will be saved to the hard disk, allowing you to resume operations anytime and pick up right where you left off.
In the worst-case scenario where your system shuts down while in hibernation mode due to a depleted battery, your work will have been saved and not lost. This is extremely useful if you know that your laptop’s battery is running out and there is no viable option to recharge it. In such cases, one can simply put the system on hibernate till the time you have the opportunity to charge and resume work again.
How to make my laptop hibernate when I close it?
You can now make your laptop hibernate by simply closing the lid. You can do so by accessing the control panel and going to the power options menu. Now choose the option called Choose what the power buttons do. In the new window that opens up, you can set your laptop to hibernate when you close the lid. You can follow our step-by-step guide with screenshots about this above — take a look at tip #2 under method 1 above.
Why hibernate option is not available?
The hibernate option is not available by default in Windows 11. The user will have to manually enable it either from the Control Panel or the Command Prompt or the Windows Registry. All three methods are perfectly viable and it is a matter of personal preference. We have covered all three methods in their entirety in the guide presented above. A quick read-through will familiarize you with the processes and allow you to access the hibernate option in no time.
Is Hibernate better than shutdown?
Hibernate is useful when you need to conserve battery power but are still working on your laptop. For example, if you are working on a project and you know that charging will be a problem in the coming days, you can choose to hibernate your system when not working to save on your battery. This allows you to come back and resume your work without your system having to shut down completely due to a depleted battery. In hibernation, your system is still technically on but it consumes very little power so it is a very handy power saving method, useful when you are in a pinch.
Shut down on the other hand completely powers off your system. This means that it ends all the applications and background activities. It also clears all the memory so resuming your work when you restart like in hibernation is not possible. It is, however, recommended to shut down your system once you are done with your work to allow clearing of the memory. This can in turn provide additional gain in performance and speed.
Related: How To Enable TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot in BIOS for Windows 11
Hibernate vs Sleep mode: How does it work?
Hibernate and sleep mode in Windows 11 are two very similar yet vastly different features. Both have their uses and work differently. Sleep mode is a power-saving mode that the system goes into. It can be comparable to pausing a video or a movie one is watching, only to resume it after a while.
In sleep mode, the system goes into a low-power state and closes all activities – background and opened ones – and all data is transferred to the memory. The system is technically still on but uses very little power in this mode. Upon resumption of normal operations, the system resumes a full-power mode within seconds, making it a viable option if the user is planning to take a short coffee break, for example.
Hibernation mode is similar to sleep mode in the sense that it also goes into a low-power setting but unlike sleep mode, the system stays off once it enters this mode. This means that the system does not consume any power in this state and is very handy especially when the battery power gets dangerously low and charging it is not an option. Hibernation mode was created mainly for laptops that run on battery power and as such may not be found on all PCs.
Another difference is that all the information is saved on the hard disk instead of the RAM, which allows the system to shut off completely. This also means that upon resumption of normal operations, the system will take longer to wake up compared to sleep mode. It is advisable to use hibernation mode only in those situations wherein the user will not be able to use the system for an extended period.
Which is better, hibernate or sleep?
It depends on how long you are going to be away from your system and even your current power situation. sleep is useful when you need to step out for a quick break from your work and will be resuming shortly. Sleep also consumes significantly more power than hibernation so this is something to keep in mind. While the resumption of work is quicker than sleep, the downside is the battery drainage.
You can use hibernate when you know you will be away from your system for a while but would like to resume your work when you open it again. It is also very handy especially when faced with low battery power. Hibernation will save all your work and then shut off the system to conserve battery. You can then carry your system with you until you reach a charging point where you can safely plug in and resume your work.
It is all dependent upon the user’s situation and requirements. Remember, use Sleep for short periods of inactivity and use Hibernate for longer periods where you need to save battery power too.
How do I know if hibernate is enabled?
The easiest way would be to go to the Start Menu and click on the power button. If Hibernate is enabled, you will see the option appear in the list. You can also access the Control Panel to find out if Hibernate is enabled on your system. If you are looking for a way to enable hibernation in your system, we have provided a complete guide to achieve the same above. It is also complete with the steps to open Control Panel and access the power options too where you can check if hibernation is enabled or not.
Is hibernate good for my laptop? Can hibernate mode harm my laptop?
Hibernation is perfectly safe for your system. It is essentially a clean and controlled shutdown of your laptop but with your active sessions or work being saved. This allows you to quickly resume your work without having to start from scratch again and is very useful to individuals who work on projects that require continuous work to be done, repeatedly. However, since hibernation saves all the data to the hard drive, it is recommended that you perform a complete shutdown and restart now and then to prevent issues related to unnecessary cache build-up and resource management. Routine startups will also enable Windows to download and install pending updates and keep your system up to date with the latest build.
How to add hibernate in Windows 11?
The hibernate option is available on Windows 11 but is not enabled by default. However, we have provided three ways above to enable the hibernate option in Windows 11 easily. The first method, using the Control Panel, is the easiest but if that doesn’t work for you for some reason,. using command prompt or Windows Registry Editor are the two other ways to go about it.
RELATED
- How to Disable VBS on Windows 11 and Does it Help?
- 3 Ways to Disable Lock Screen on Windows 11
- How to Disable Windows Search on Windows 11
- Where is ‘My Computer’ on Windows 11? How to Find ‘This PC’ Easily!
- How to Disable Web Results in Windows 11 Start or Search Menu
- How to Enable Virtualization in BIOS on Windows 11 or 10




With all that has been said in this helpful Article, the problem still remains as to Windows automatically going into Hibernate on its own. In other words, it doesn’t. Why Hibernate was removed from Windows 11, is about anyone’s guess, including the individual who started the ball rolling with it at Microsoft.