What to know
- Administrative Tools have been relegated to the background on Windows 11. But they can still be accessed via the Control Panel (Large icons > Windows Tools), via RUN (control admintools), and the Start menu.
- Terminal apps like Command Prompt and PowerShell also make up easy ways to navigate to Administrative Tools. Use the command
control admintoolsfor both. - You can also paste
%ProgramData%\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Administrative Toolsinto File Explorer’s address bar to reach Administrative Tools.
Windows Administrative Tools allow you to view ongoing processes, keep track of logs and events, adjust services and tasks on your PC, and a lot more.
But with Windows 11, a lot of things have changed for Administrative Tools and users may find it difficult to locate them. If you’re in the same boat then here’s all you need to know about administrative tools in Windows 11.
How to access Administrative Tools on Windows 11
You can access Administrative Tools or Windows Tools on Windows 11 in 7 different ways. Follow either of the sections below depending on your current preferences and requirements.
Method 1: Using the Control Panel
The tried and tested way of accessing Administrative Tools from the Control Panel still works. You will find them under their new name when launching Control Panel.
- Press
Windows + Rto launch Run. Type control and hit Enter.
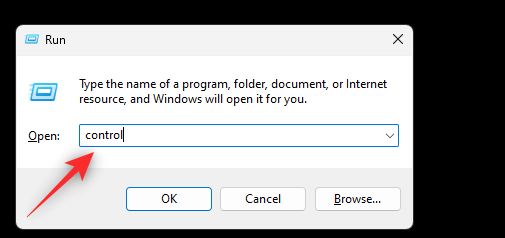
- Click the drop-down menu in the top right corner and select Large icons.
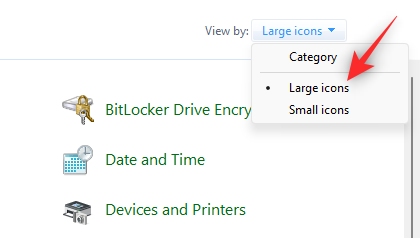
- Click Windows Tools at the bottom.

- A new folder will now open within File Explorer containing your old Administrative Tools and new Windows Tools, all in one location. Double-click and launch the preferred tool to manage your PC.
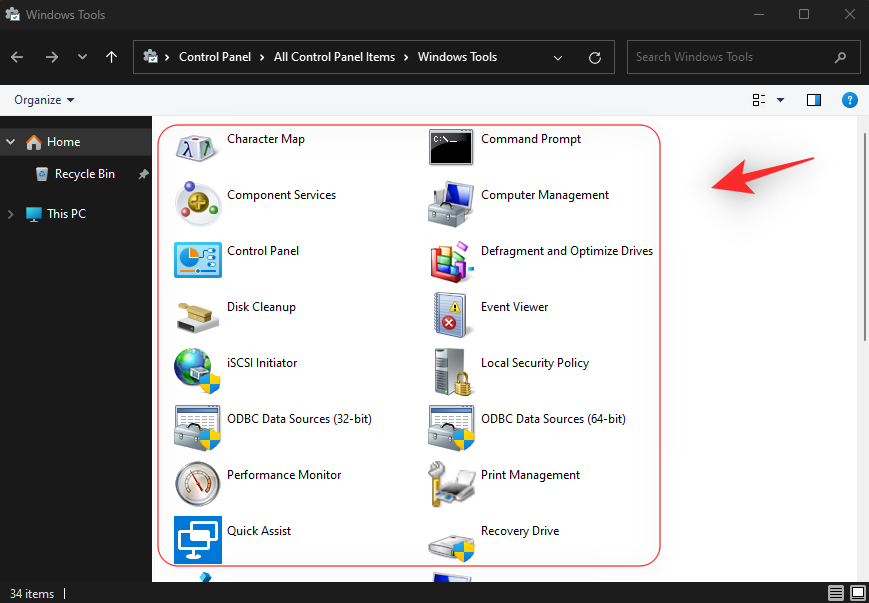
And that’s how you can access Windows Tools from the Control Panel.
Method 2: Using Run
You can also use Run to launch Windows tools from anywhere on your PC. Follow the steps below to help you along with the process.
- Press
Windows + Rto launch Run. Then type in the following and press Enter:control admintools
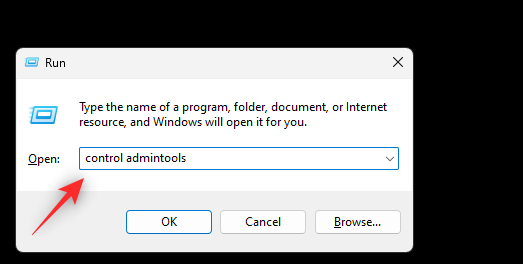
Note: You can also use the commandshell:control administrative tools. However, this will open the old list of Administrative Tools without the new addition to Windows Tools in Windows 11. - A new window will now launch on your PC showing you the list of Windows Tools.
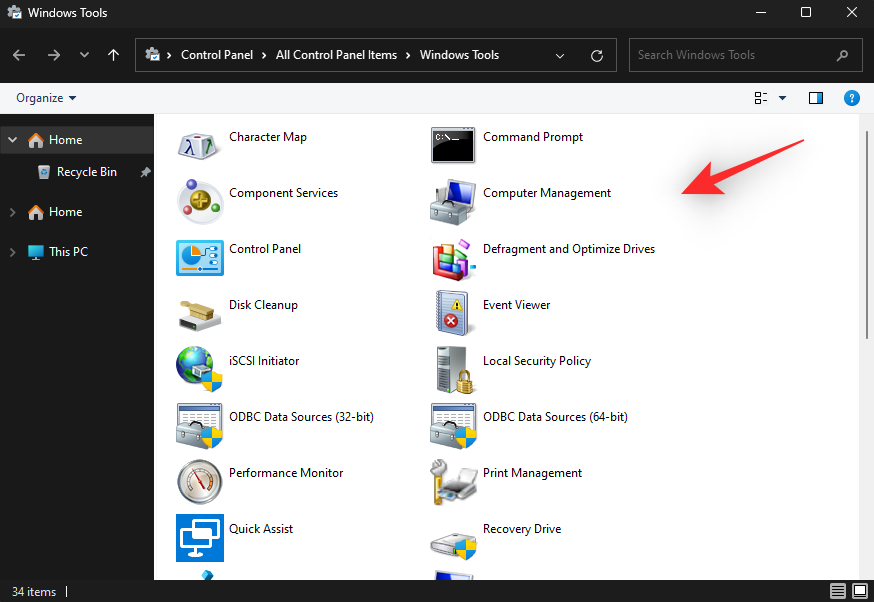
And that’s how you can access Windows Tools using Run.
Method 3: Using the Search/Start menu
- Launch the Start menu, type in Windows tools, and launch the same from your search results.
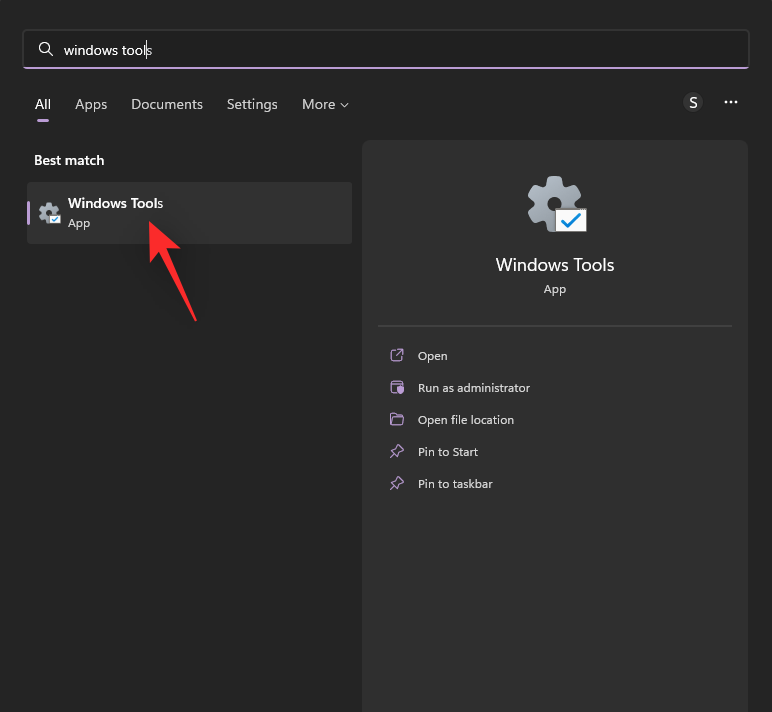
- A new window will now open with the new list of Windows Tools available in Windows 11.

Method 4: Using File Explorer
Here’s how to use the File Explorer to reach Administrative Tools (aka Windows Tools):
- Press
Win+Eto open the File Explorer. - Then copy and paste the following address into the address bar:
%ProgramData%\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Administrative Tools
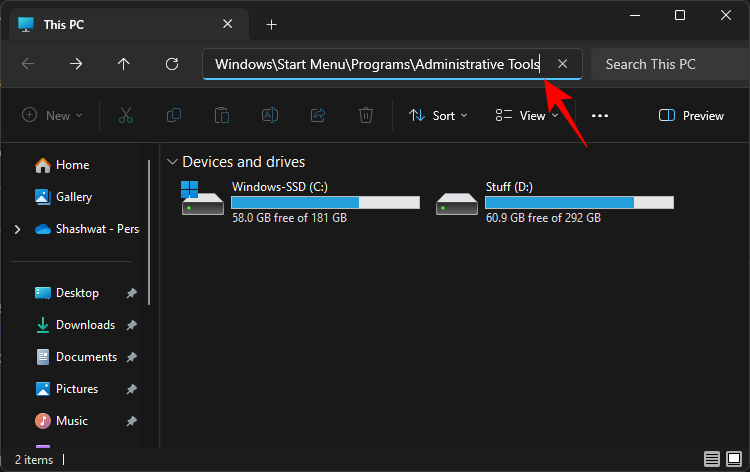
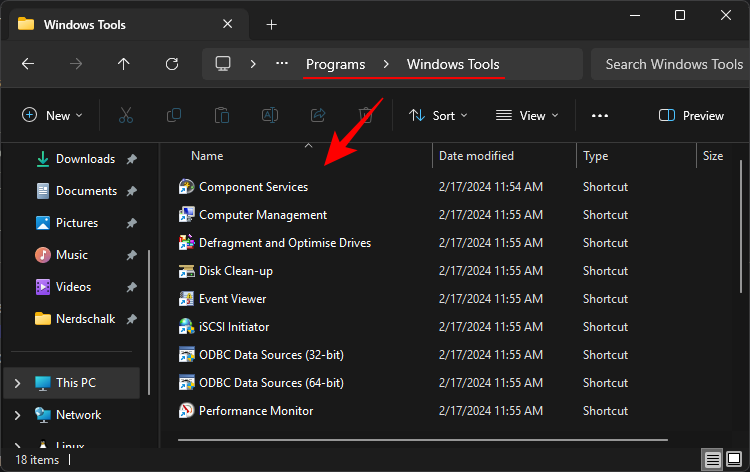
- Hit Enter and you will be directed to Windows Tools.
Method 5: Using CMD
Here’s how you can access Windows Tools using the Command Prompt. Follow the steps below to help you along with the process.
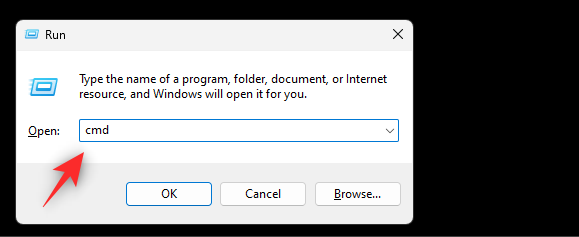
- Press
Windows + Rto launch Run. Type cmd andCtrl + Shift + Enter.
- Now use the following command to access Windows Tools:
control admintools
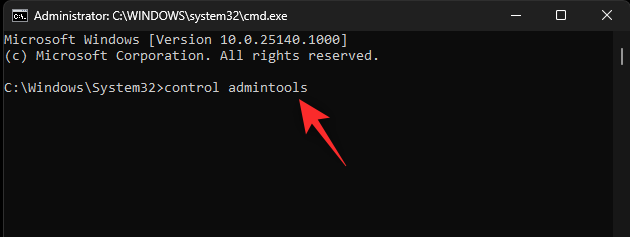
- You will now have a File Explorer window with the Windows Tools open on your screen.

And that’s how you can access Windows Tools using the Command Prompt.
Method 6: Using PowerShell
You can also use PowerShell to access Windows Tools on your PC. Here’s how you can get started.
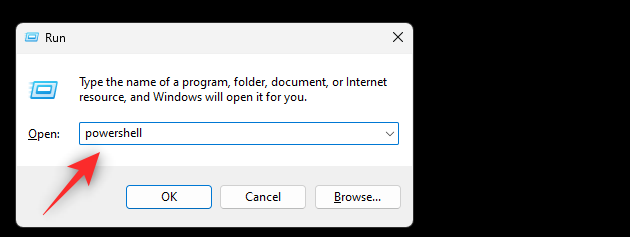
- Press
Windows + Rto launch the Run dialog box. Type powershell and pressCtrl + Shift + Enter.
- Type in the following to open Windows Tools:
control admintools
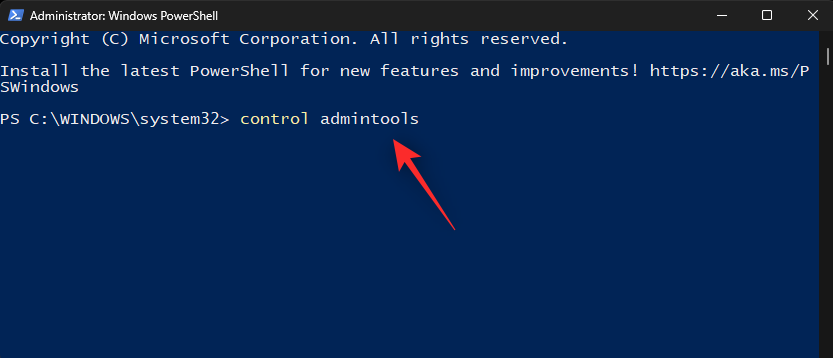
- A new window with Windows Tools will now open on your screen.

Method 7: Using a custom shortcut
You can also create a custom shortcut in a preferred location to access Windows Tools whenever needed. Here’s how you can get started.
Note: These shortcuts will open the old Windows 10 list of Administrative Tools instead of the new Windows Tools list.
- Open the desired location where you wish to place your Windows Tools shortcut. We will be using the desktop for this example. Right-click on an empty area and select New.
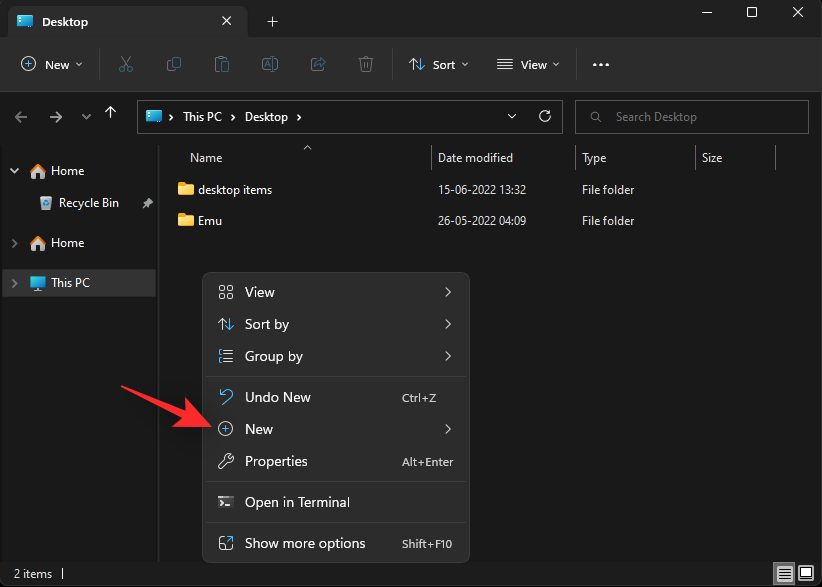
- Click Shortcut.
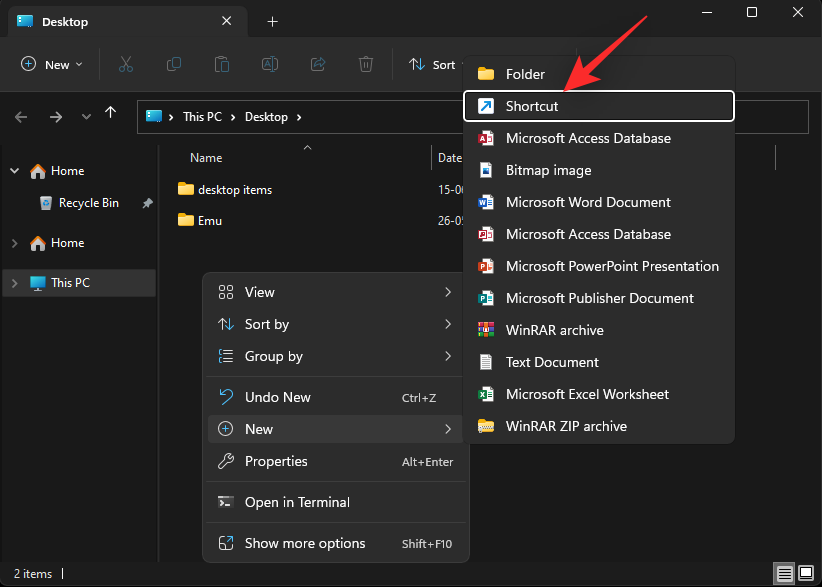
- Now copy and paste either of the paths below in the text box.
Path 1:C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Administrative Tools
Path 2:%ProgramData%\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Administrative Tools
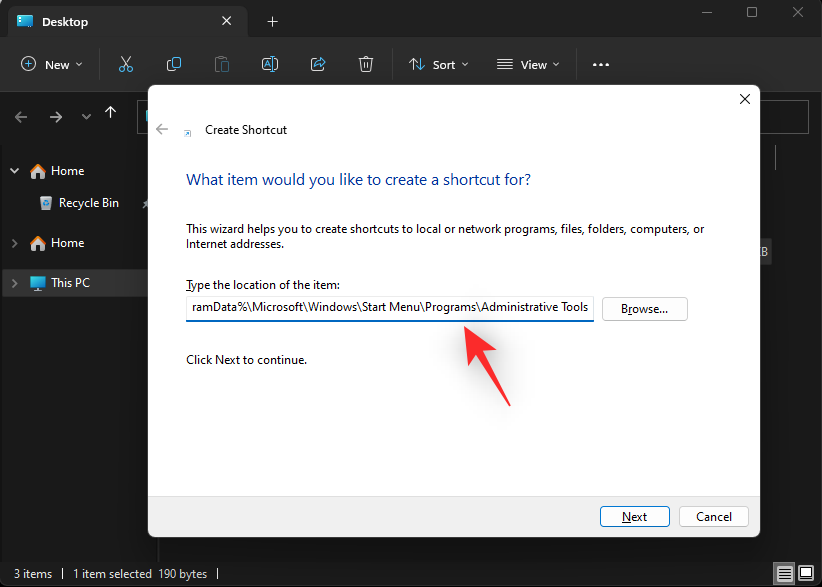
- Click Next.
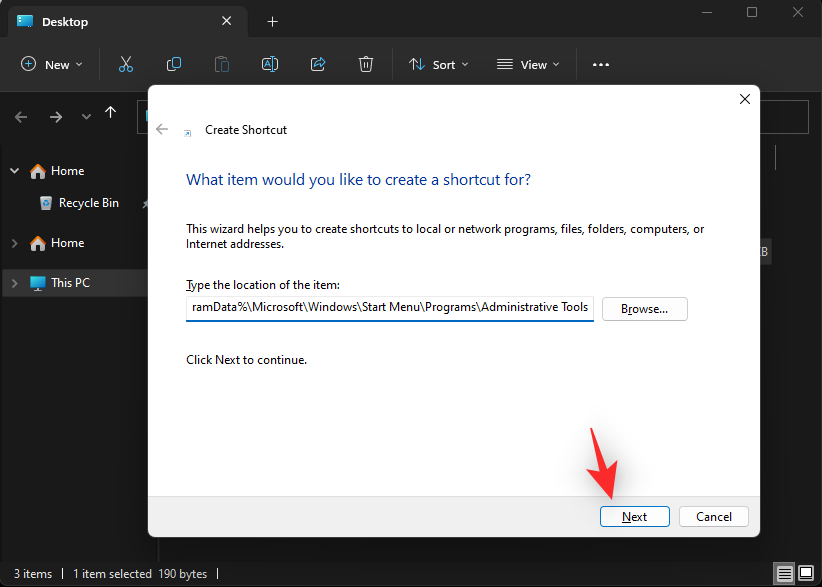
- Type in a custom name for your shortcut if you’d like.
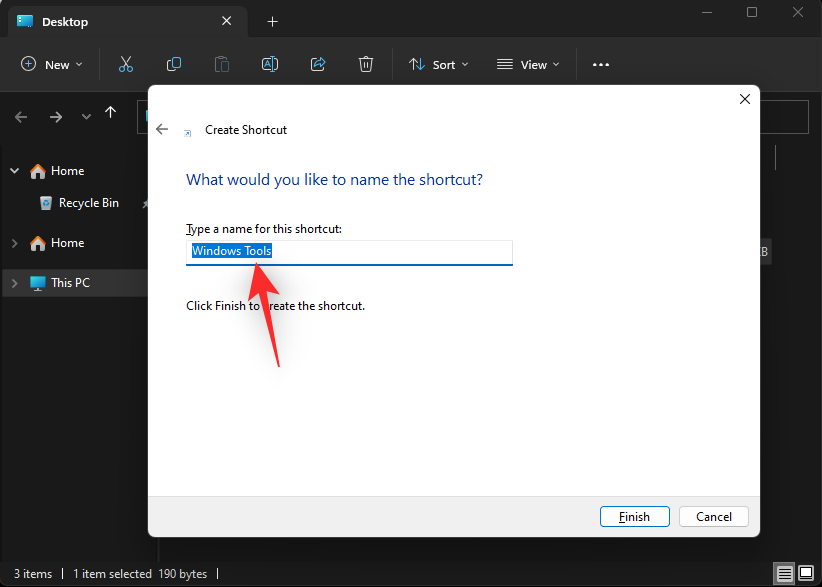
- Click Finish once you’re done.
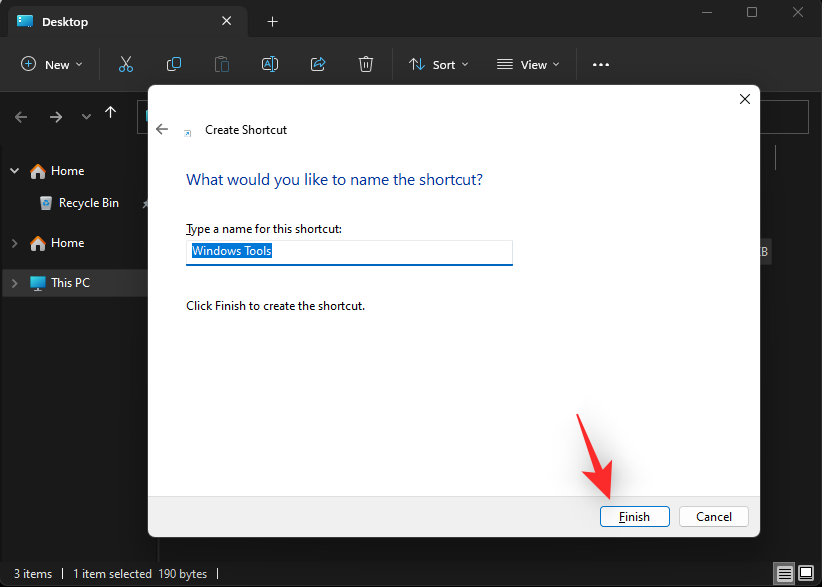
And that’s it! You will now have created a shortcut to Windows Tools in the desired location.
Windows Tools offered in Windows 11
Here are all the Windows Tools offered in Windows 11. We have included a CMD command to help you launch the same from anywhere on your desktop.
Character Map
- CMD command:
%windir%/system32/charmap.exe
Command Prompt
Command Prompt is the default command-line interpreter in Windows. We recommend you launch it using the Run utility. Follow the steps below to help you along with the process.
Press Windows + R to launch Run.
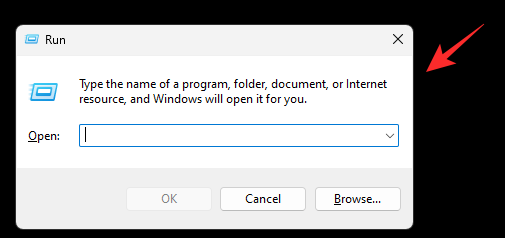
Type in the following.
cmd

Now press one of the following depending on your preferences.
Enter: This will launch CMD as a current local user.Ctrl + Shift + Enter: This will launch CMD as an administrator for the current PC.
You will now have launched CMD on your PC.
Component Services
- CMD command:
%windir%/system32/dcomcnfg.exe
Computer Management
- CMD command:
%windir%/system32/CompMgmtLauncher.exe
Control Panel
- CMD command:
%windir%/system32/control.exe
Defragment and Optimize Drives (old)
- CMD command:
%windir%/system32/defrag.exe
Disk Cleanup (old)
- CMD command:
%windir%/system32/cleanmgr.exe
Event Viewer (old)
- CMD command:
%windir%/system32/eventvwr.exe
iSCSI Initiator (old)
- CMD command:
%windir%/system32/iscsicpl.exe
Local Security Policy (old)
- CMD command:
%windir%\system32\secpol.msc /s
ODBC Data Sources (32-bit & 64-bit) (old)
- CMD command:
%windir%\syswow64\odbcad32.exe
Performance Monitor (old)
- CMD command:
%windir%\system32\perfmon.msc /s
Print Management (old)
- CMD command:
%systemroot%\system32\printmanagement.msc
Quick Assist
- CMD command:
%windir%\system32\quickassist.exe
Recovery Drive
- CMD command:
%windir%\system32\RecoveryDrive.exe
Registry Editor
- CMD command:
regedit
Remote Desktop Connection
- CMD command:
mstsc
Resource monitor (old)
- CMD command:
%windir%\system32\perfmon.exe /res
Run
Simply use Windows + R to launch Run from anywhere in Windows 11.
Services (old)
- CMD command:
%windir%\system32\services.msc
System Configuration (old)
- CMD command:
%windir%\system32\msconfig.exe
System Information (old)
- CMD command:
%windir%\system32\msinfo32.exe
Task Manager
Use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Shift + Esc to launch Task Manager from anywhere within Windows 11.
Task Scheduler (old)
- CMD command:
%windir%\system32\taskschd.msc /s
Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security (old)
- CMD command:
%windir%\system32\WF.msc
Windows Fax and Scan
- CMD command:
%windir%\system32\WFS.exe
Windows Media Player Legacy
- CMD command:
"%ProgramFiles(x86)%\Windows Media Player\wmplayer.exe" /prefetch:1
Windows Memory Diagnostic (old)
- CMD command:
%windir%\system32\MdSched.exe
Windows PowerShell (x64 & x86) (old)
- CMD command:
powershell
Note: If you wish to launch PowerShell separately, use the same command in Run instead.
Windows PowerShell ISE (x64 & x86) (old)
- CMD command:
%windir%\system32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\PowerShell_ISE.exe
Wordpad
- CMD command:
"%ProgramFiles%\Windows NT\Accessories\wordpad.exe"
We hope this guide helped you get familiar with the new Windows tools in Windows 11. If you face any issues or have any more questions, feel free to reach out using the comments below.











Discussion